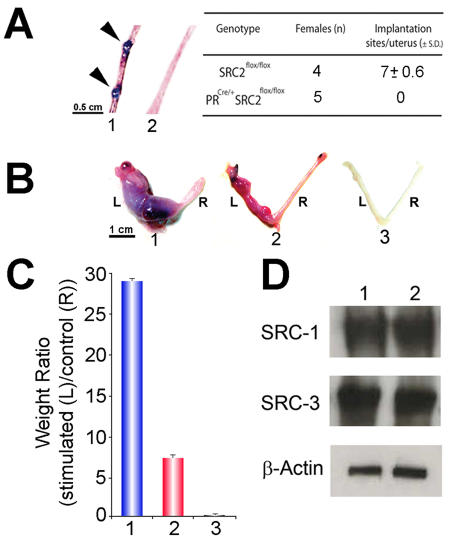
Figure 2. Abrogation of uterine SRC-2 results in a block in embryo implantation and a partial decidual response.
In panel A, arrows show the location of implantation sites in the uterus (1) of a SRC-2flox/flox (or wild-type (WT)) mouse (5.5 days post coitum (d.p.c.)). However, implantation sites were not detected in uteri from similarly treated PRCre/+SRC-2flox/flox (2) mice. The average number of implantation sites per genotype per total number of mice examined is tabulated. In panel B, the gross morphological response of the left (L) uterine horn to a deciduogenic stimulus for SRC-2flox/flox (1), PRCre/+SRC-2flox/flox (2), and PRCre/+SRC-2flox/flox SRC-1KO trigenic (3) mice is shown. The right (R) uterine horn represents the unstimulated control. Although the PRCre/+SRC-2flox/flox uterus (2) exhibits a limited decidual response, note the absence of a decidual response in the PRCre/+SRC-2flox/flox SRC-1KO trigenic uterus (3). Panel C graphically presents the average weight ratios (± standard deviation (SD)) of stimulated (L) to control (R) horn for SRC-2flox/flox (1), PRCre/+SRC-2flox/flox (2), and PRCre/+SRC-2flox/flox SRC-1KO trigenic (3) uteri. Western analysis in panel D reveals uterine tissue from untreated adult virgin SRC-2flox/flox (1) and PRCre/+SRC-2flox/flox (2) mice show equivalent levels of uterine SRC-1 and SRC-3 (loading control is β-actin). Modified from (Mukherjee et al., 2006b) (Copyright (2006) American Society for Microbiology).