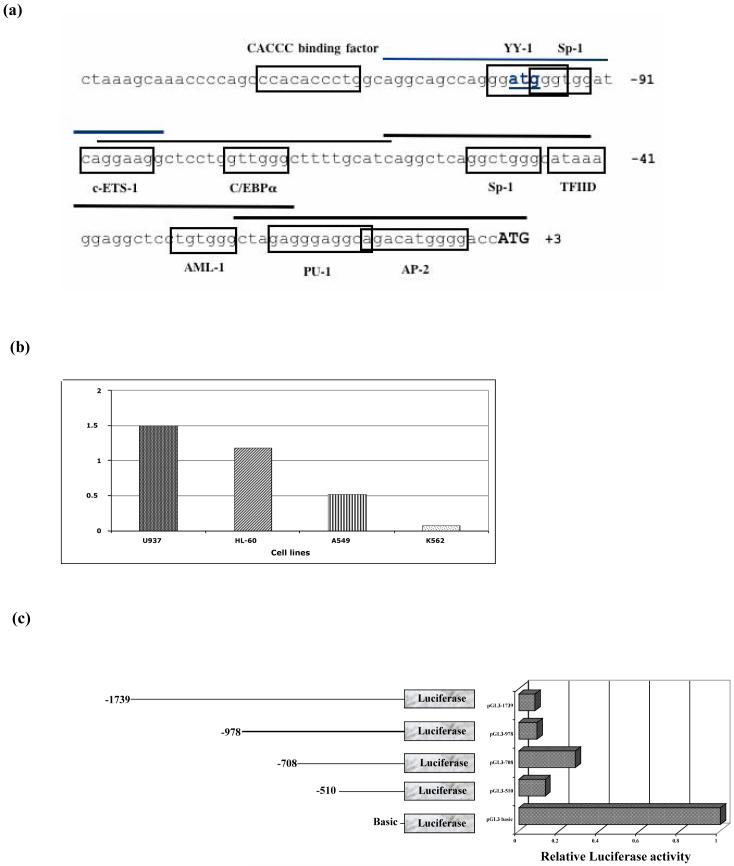
Fig. 3.
Computational analysis of hCAP18 promoter and assessment of its activity in transiently transfected K562 cells. (a) Nucleotide sequence of the 5′ flanking region of hCAP18. Putative transcription factor binding sites are boxed. Translational start is shown in bold as well as the upstream ATG. Sequences used for EMSA oligonucleotide probes are indicated by bars. The nucleotides are numbered relative to the translation initiation codon. (b) The pGL3-1739/-1 construct was transfected into four different cell lines (U937, HL-60, A549 and K562 cells), then assayed for luciferase activity after 18 hours. Values shown are relative fold increase compared to basic and normalized to Renilla activity. (c) The 5′ deletion constructs as shown in the diagram, are transfected into K562 cells, and assayed for luciferase activity after 18 hours of culture. The pGL3-1739/-1 construct as well as the 5′ deletion constructs yielded reproducibly lower luciferase activity than the promoterless reporter alone.