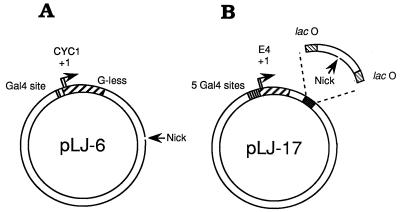
Figure 2.
The transcription templates. (A) pLJ-6 contains the S. cerevisiae CYC1 promoter and a G-less cassette transcription unit. G-less transcripts initiating at CYC1 are ≈350 and ≈370 nt in length (35, 36). A DNA-loading site for β–VP16 is generated by cutting the nontemplate strand of this transcription unit with phage fd gpII endonuclease. In pLJ-5, the resulting DNA nick is located in the template strand. (B) pLJ-17 and -18 contain five Gal4-binding sites immediately upstream of the adenovirus E4 core promoter (base pairs −38 to +250 relative to the major transcriptional start site). The gpII nicking site is located between two symmetrical lac operators (37, 38), ≈390 bp from the RNA start site. The nick is in the transcribed strand for pLJ-17 and in the nontranscribed strand for pLJ-18. In plasmids pLJ-19 and -20, the nicking site is located ≈2 kbp from the RNA start site of the E4 promoter, in the transcribed strand for pLJ-19 and in the nontranscribed strand for pLJ-20. R3 Lac repressor, which forms a homodimer, and is, as a consequence, monovalent for DNA-binding (39, 40), was used to confine sliding clamps loaded at the single nick of pLJ-17 and -18 to an ≈100-bp DNA segment. Confinement was relieved by adding isopropyl β-d-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) (41, 42).