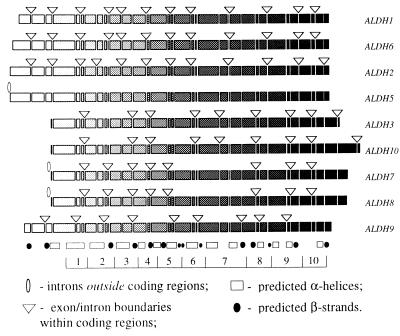
Figure 1.
Exon/intron structures of human ALDH genes mapped to the alignment of their amino acid sequences. The sequences themselves are shown as shaded rectangles, where the shading intensity increases in direction from the N to C terminus of the protein; deletions and insertions are not shown. Each discontinuity in rectangles corresponds to an exon/intron boundary observed in at least one of the genes; triangles and ellipses indicate only those introns that are actually found in the corresponding gene. Also shown is the predicted secondary structure that is assumed to be similar for all compared proteins: the hatched boxes indicate α-helices and the solid circles correspond to β-strands. The secondary structure was predicted with a neural network algorithm implemented by the PHD program (30, 31). The bottom of the figure shows an artificial segmentation of the protein into the 10 domains that were used in the computation of likelihood values.