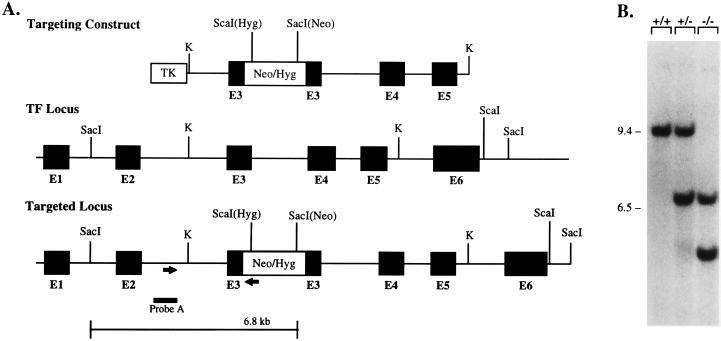
Figure 2.
Disruption of the mTF gene in ES cells. (A) Targeting constructs consist of a 5.9-kb KpnI 129/Sv genomic fragment containing mTF exons 3–5 cloned into the KpnI (K) site of pBluescript II KS(+). Inserted at the 5′ end of the mTF gene fragment is a 1.8-kb hsv-TK gene. Either a 1.5-kb pgk-Neo expression cassette or a ≈2.0-kb pgk-Hyg expression cassette was inserted into an introduced unique XhoI (X) site in exon 3. Homologous recombination with the mTF alleles introduces a new SacI (for Neo construct) or ScaI (for Hyg construct) site into the mTF locus. Arrows indicate the PCR primers used in screening ES cell colonies for homologous recombination with the Neo construct. Digestion of genomic DNA with SacI/ScaI yields a wild-type mTF allele at ≈11 kb and targeted alleles at ≈6.8 kb (Neo construct) and/or ≈5.8 kb (Hyg construct). (B) Southern blot analysis using probe A of SacI/ScaI-digested DNA prepared from wild-type ES cells (+/+), ES cells targeted with the Neo construct (+/−), or ES cells targeted with both the Neo and Hyg constructs (−/−).