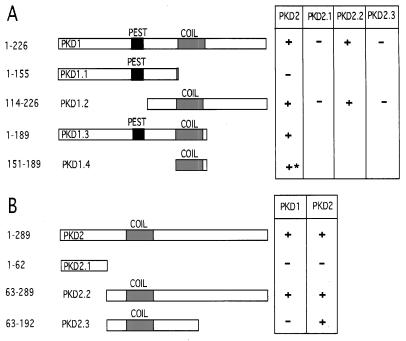
Figure 1.
Mapping the heterodimerization domains of PKD1 and PKD2 (A) and the homodimerization domains of PKD2 (B) in the yeast two-hybrid system. (A) The C-terminal 226 amino acids of PKD1 and progressive C- and N-terminal deletions of this domain were inserted into pLEX. For PKD2 binding assays, the pLex bait constructs and PKD2 prey constructs were sequentially transfected into the yeast strain EGY48 bearing a lacZ reporter. Interaction (+) was indicated by β-galactosidase production and leucine prototrophy in yeast; the minimal interacting domain, PKD1.4, caused leucine prototrophy without β-galactosidase production (∗). A putative coiled–coil structure is depicted as a shaded box, a potential PEST sequence is depicted as a solid box. (B) The C-terminal 289 amino acids of PKD2 and progressive C- and N-terminal deletions of this domain were inserted into pLEX to map the interaction with PKD1 and PKD2. PKD2 binds PKD1 through the C-terminal 97 amino acids. The homodimerization of PKD2 is mediated by a region spanning amino acids 63–192, which contains a putative coiled–coil structure (shaded box).