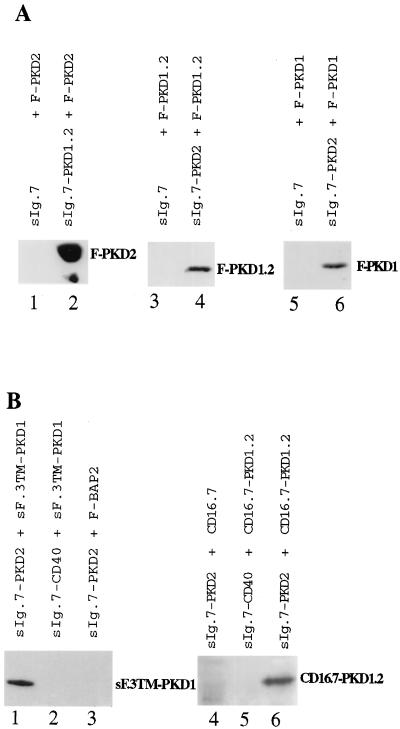
Figure 4.
Heterodimerization of PKD1 and PKD2 in vivo. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation of membrane-bound chimeric PKD1 and PKD2 proteins with cytoplasmic PKD2 and PKD1 fusion proteins, respectively. 293T cells were transfected with the indicated combinations of expression vectors for PKD1 and PKD2, and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with protein A, followed by Western blot analysis with anti-FLAG. sIg.7–PKD1.2 interacted with F–PKD2 (lane 2) but not with the sIg.7 control protein (lane 1). The interaction between sIg.7–PKD2 and F–PKD1.2 is demonstrated in lane 4; the interaction between sIg.7–PKD2 and F–PKD1 is shown in lane 6. Neither F–PKD1.2 nor F–PKD1 interacted with the sIg.7 control protein. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of membrane-bound fusion proteins of PKD2 and PKD1. 293T cells were transfected with the expression vectors indicated above. Immunoprecipitations were performed with protein A, followed by Western blot analysis with anti-FLAG (lanes 1–3) or anti-CD16 (lanes 4–6). Lane 1 demonstrates the interaction with sIg.7–PKD2 and sF.3TM–PKD1. No interaction was detectable between sF.3TM–PKD1 and sIg.7–CD40 or between sIg.7–PKD2 and F–BAP2. Lane 6 shows the interaction between the two membrane-bound fusion proteins CD16.7–PKD1.2 and sIg.7–PKD2. No interaction was detectable with the control proteins CD16.7 (lane 4), or sIg.7–CD40 (lane 5).