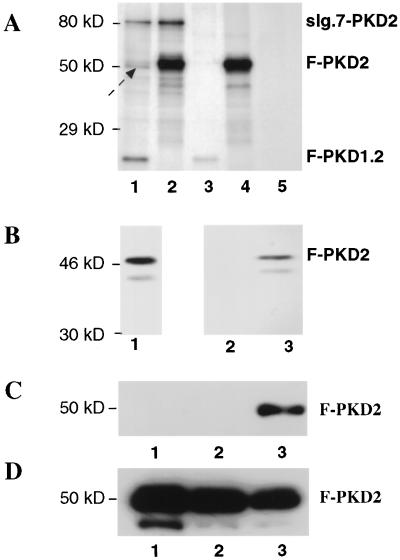
Figure 5.
Hetero- and homodimerization of PKD1 and PKD2. (A) Coimmunoprecipitations of 35S-labeled PKD1 and PKD2 fusions proteins. 293T cells were transfected with sIg.7–PKD2 and F–PKD1.2 (lane 1), sIg.7–PKD2 and F–PKD2 (lane 2), sIg.7 and F–PKD1.2 (lane 3), sIg.7 and F–PKD2 (lane 4), or remained untransfected (lane 5). Cells were harvested after a 6-hr chase with [35S]methionine/cysteine. Immunoprecipitations were performed with anti-FLAG M2 affinity gel. The arrow marks a putative 50-kDa protein present in lane 1 (and potentially in lanes 2 and 4), which appears to associate with PKD2 or the PKD1–PKD2 complex. Similar results were obtained with reciprocal immunoprecipitation using protein A to immunoprecipiate the IgG-tagged constructs (data not shown). (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of 35S-labeled F–PKD2 with MBP–PKD1.2 fusion protein. F–PKD2 was in vitro transcribed and translated (lane 1). An aliquot of the reaction mixture was then incubated with a control MBP–protein (lane 2) or MBP–PKD1.2 (lane 3). (C) Homodimerization of PKD2 in vivo. 293T cells were cotransfected with sIg.7 and F–PKD2 (lane 1), sIg.7–CD40 and F–PKD2 (lane 2), and sIg.7–PKD2 and F–PKD2 (lane 3). Lysates were immunoprecipitated with protein A, and bound proteins were blotted with anti-FLAG. (D) Cell lysates demonstrating comparable expression of the F–PKD2 fusion protein in all three conditions (lanes 1–3 as in C).