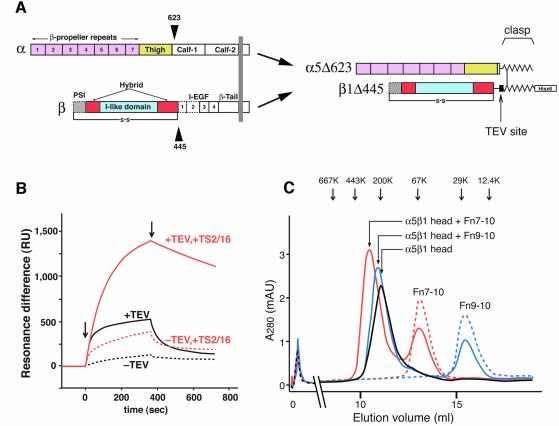
Fig. 1. The truncated α5β1 headpiece retains its functional integrity. (A) The domain organization within the primary structure of integrin α5β1 is shown on the left, and the design of the recombinant soluble α5β1 headpiece is shown on the right. Disulfide-bonded α-helical coiled-coil domains were attached to the C-termini of the truncated subunits to act as a clasp (Takagi et al., 2001). Domains included in the headpiece fragment are color coded as follows: α5 β-propeller repeat domain in pink, α5 thigh domain in yellow, β1 PSI domain in gray, β1 I-like domain in cyan and β1 hybrid domain in red. Domains not resolved in the crystal structure are depicted by dotted lines, and the position of the long-range disulfide bond present in the β subunit is shown below. (B) Binding analysis of Fn9–10 to the α5β1 head fragment by surface plasmon resonance. Clasped (–TEV, dotted lines) or unclasped (+TEV, solid lines) α5β1 headpieces were preincubated with (red lines) or without (black lines) a 3-fold molar excess of TS2/16 Fab fragment for more than 10 min and infused at a concentration of 50 nM onto the sensor surface coated with 650 RU of Fn9–10. Arrows indicate start- and end-points of the injections. (C) Gel filtration chromatography of the α5β1 headpiece with bound ligands. The TEV-cleaved α5β1 headpiece (∼70 pmol) was incubated with 150 pmol of Fn9–10 (blue), Fn7–10 (red) or without ligands (black) in the presence of 1 mM Mn2+ for 1 h and separated on a Superdex 200 column. Chromatograms for 150 pmol Fn7–10 (red dotted) or Fn9–10 (blue dotted) alone are also shown. The elution positions of standard proteins are indicated by arrows (667 kDa, thyroglobulin; 443 kDa, apoferritin; 200 kDa, β-amylase; 67 kDa, serum albumin; 29 kDa, carbonic anhydrase; 12.4 kDa, cytochrome c).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.