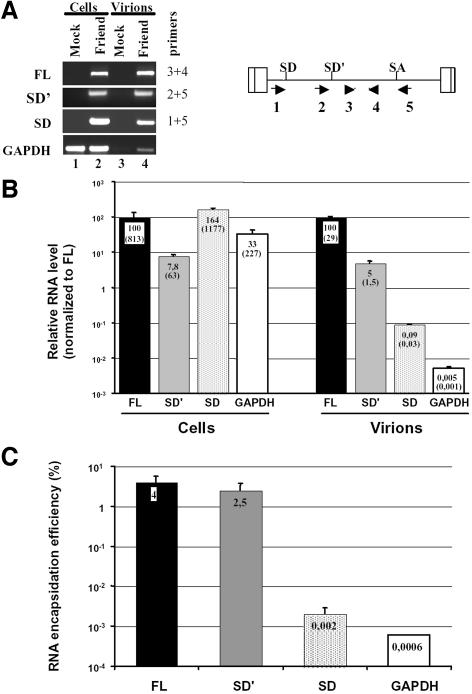
Fig. 2. Measure of SD′ RNA content in replication-competent MLV infected M.dunni cells and virions by real-time RT-PCR. (A) Analysis of RT-PCR products by agarose gel electrophoresis. Viral RNA components were extracted from either infected cells or virions, and were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR. From a unique RT reaction, four different PCRs were performed specific to each RNA species: genomic (FL), alternatively spliced (SD′), canonically spliced (SD) and control GAPDH mRNA. Approximate positions of the primers used to amplify the different RNA species are indicated by the numbered arrows. Mock samples correspond to similar experiments conducted with non-infected cells. Amplified samples were loaded on agarose gel and stained by ethidium bromide. Each RNA species detected is indicated on the left side of the gel, with corresponding oligonucleotide pairs identified by numbers on the right. (B) Results of quantitative RT-PCR experiments. Relative levels of FL (fixed to 100), SD′ and SD RNA in both chronically infected cells and virions were determined as described in Materials and methods. Values represent average of at least three independent RT-PCR assays with standard deviations. Absolute quantification values (parentheses) are expressed as RNA copy number per infected cell. (C) RNA encapsidation efficiency of each viral RNA species. Final encapsidation levels were calculated as the ratio of viral to cellular RNA values obtained in (B) and expressed as a percentage.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.