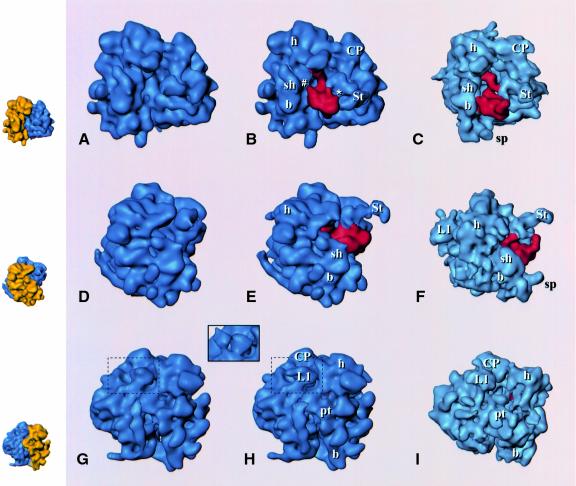
Fig. 2. Reconstructions of the 80S ribosome from S.cerevisiae without (A, D, G) and with (B, E, H) EF2 bound, and the EF-G-bound 70S ribosome from E.coli (C, F, I; adapted from Agrawal et al., 1999), presented in three equivalent views. Upper row (A–C): side view, with small subunit on the left and large subunit on the right, showing the binding sites of the elongation factors; middle row (D–F): view from the small subunit solvent side, with (E) and (F) showing the extended stalk (St); bottom row (G–I): view from the L1 protein side. The inset above (G) and (H) shows a comparison of the L1 region [within the dashed boundary in (G) and (H)] with the ‘split’ appearance of L1 in the yeast ribosome in a previous reconstruction (Beckmann et al., 1997). EF2 and EF-G are shown in red. Small insets on the left depict the 80S control map with 40S and 60S colored in yellow and blue, respectively, in corresponding orientations as an interpretation aid. Landmarks, small subunit: h, head; b, body; pt, platform; sh, shoulder (for the designation of subunit body, see Figure 3; large subunit: CP, central protuberance; L1, L1 protuberance; St, extended stalk.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.