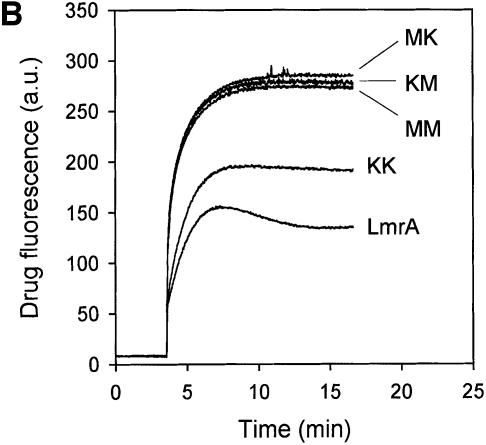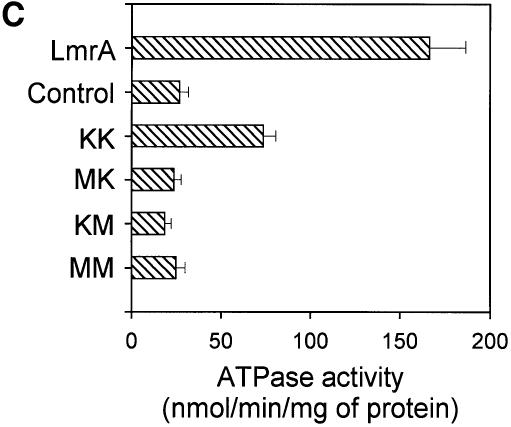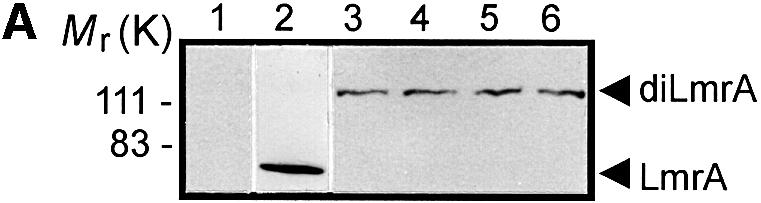
Fig. 1. Expression and activity of covalently linked dimers of LmrA. (A) Western blot of total membrane protein (20 µg) from inside-out membrane vesicles lacking LmrA (lane 1), or containing LmrA (lane 2), the wild-type (KK) form of dimeric LmrA (lane 3), or the dimeric form of LmrA with a K to M substitution in the Walker A region of the first ABC domain (MK, lane 4), the second ABC domain (KM, lane 5), or both ABC domains (MM, lane 6). The western blot was probed with an anti-His6 tag antibody. The migration of molecular mass markers is indicated. An arrowhead indicates the position of monomeric LmrA (66 kDa) and dimeric LmrA (132 kDa). (B) Accumulation of ethidium bromide in cells expressing LmrA, or the KK, MK, KM or MM forms of dimeric LmrA. Cells were pre-energized for 3.5 min in the presence of 20 mM glucose, after which 2 µM ethidium bromide was added. Ethidium accumulation in the cells was measured by fluorimetry. The uptake of ethidium in control cells not expressing LmrA was similar to that in cells expressing the KM, MK or MM form of dimeric LmrA (not shown). (C) Vanadate-sensitive ATPase activity in inside-out membrane vesicles lacking LmrA (control), or containing LmrA, or the KK, MK, KM or MM form of dimeric LmrA. The ATPase activity was measured at a Mg-ATP concentration of 1 mM in the presence of 20 µM verapamil.