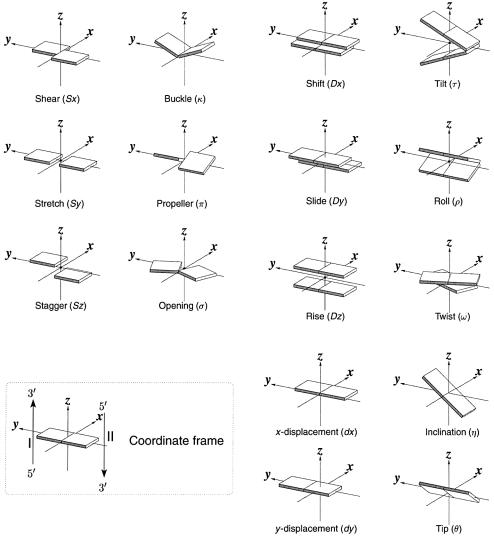
Figure 1.
Pictorial definitions of rigid body parameters used to describe the geometry of complementary (or non-complementary) base pairs and sequential base pair steps (19). The base pair reference frame (lower left) is constructed such that the x-axis points away from the (shaded) minor groove edge of a base or base pair and the y-axis points toward the sequence strand (I). The relative position and orientation of successive base pair planes are described with respect to both a dimer reference frame (upper right) and a local helical frame (lower right). Images illustrate positive values of the designated parameters. For illustration purposes, helical twist (Ωh) is the same as Twist (ω), formerly denoted by Ω (19,20) and helical rise (h) is the same as Rise (Dz).