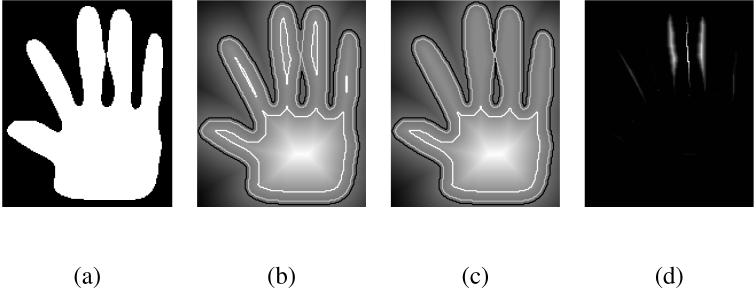
Fig. 3.
A 2D example: from the outline of a hand (a), we build a signed distance function (b). Notice from the outlined isocontours how the topology of the object changes as the fingers get separated from the palm or merge. The topology-preserving approximation (c) is very similar to the original distance function, but maintains the same topology for all isovalues. The difference f - g (d) is zero almost everywhere, and small otherwise (the amplitude of the difference image is about 5% of the amplitude of the original distance function).