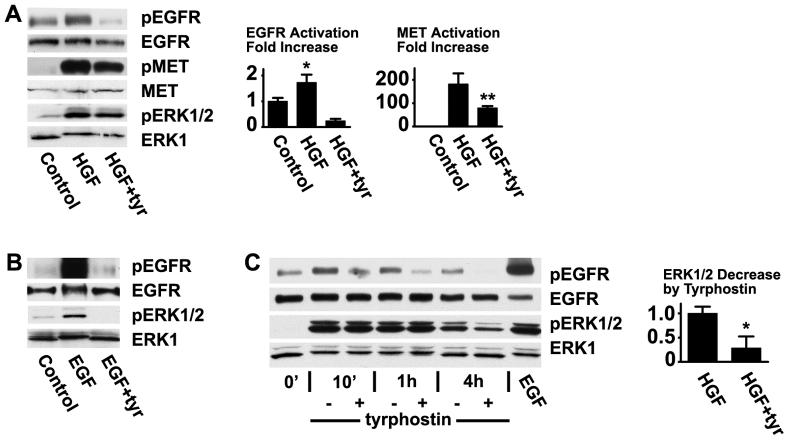
Fig. 1.
Activation of the EGFR by HGF in corneal epithelial cells. (A) HCLE cells were treated with 10 ng/ml HGF for 10 minutes, the extracts were immunoblotted with an antibody that recognizes the EGFR phosphorylated on tyr-1173, and the blots were stripped and subsequently blotted with an antibody that recognizes the total amount of EGFR. The same blots were immunoblotted with an antibody that recognizes activated ERK1/2. The extracts were also immunoblotted with antibodies against MET and MET phosphorylated on tyr-1234/1235. Where indicated, 10 μM tyrphostin AG 1478 was added for 15 minutes before treatment. The bar graph shows the results of densitometry of the autoradiograms. The values in this and the following figures are means of triplicates or more, and the error bars are standard deviations. Analysis by the students's t test for unpaired samples showed significant increase of the signal from the EGFR in response to HGF (*, P<0.005). The signal from MET in response to HGF was significantly reduced in the presence of tyrphostin AG 1478 (**, P<0.005) (B) Cells were treated with 100 ng/ml EGF, and processed similarly. (C) Cells were treated for the indicated times and extracts immunoblotted as in (A). pERK1/2 was significantly reduced in the presence of tyrphostin AG 1478 (*, P<0.0005).