Fig. 2.
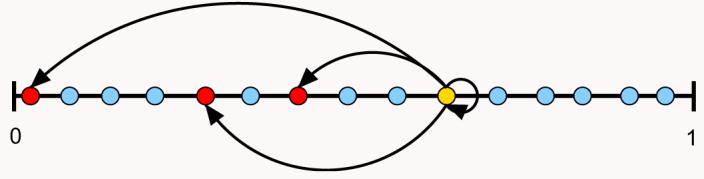
The generalized cascade model of Stouffer et al. (2005). In the generalized cascade model species make up an ordered set according to their niche value n, 0<n<1. Each species i then consumes species j with nj≤ni with a probability x drawn at random from a probability distribution p(x) given by the beta-distribution Eq. (1). In this example the predator (the yellow species) can consume any of the species to its left on the axis, including itself. In this case, x ≈ 0.2 and the yellow predator consumes itself and three other species.
