Figure 3. Effect of activation of PKC by PMA on the relaxation response to cumulative concentrations of acetylcholine (ACh) in intact aortic rings from male (A) and female (B) rats, and the effect of pretreatment of rings with LY379196, Fasudil, Ro-32-0432, or Rottlerin.
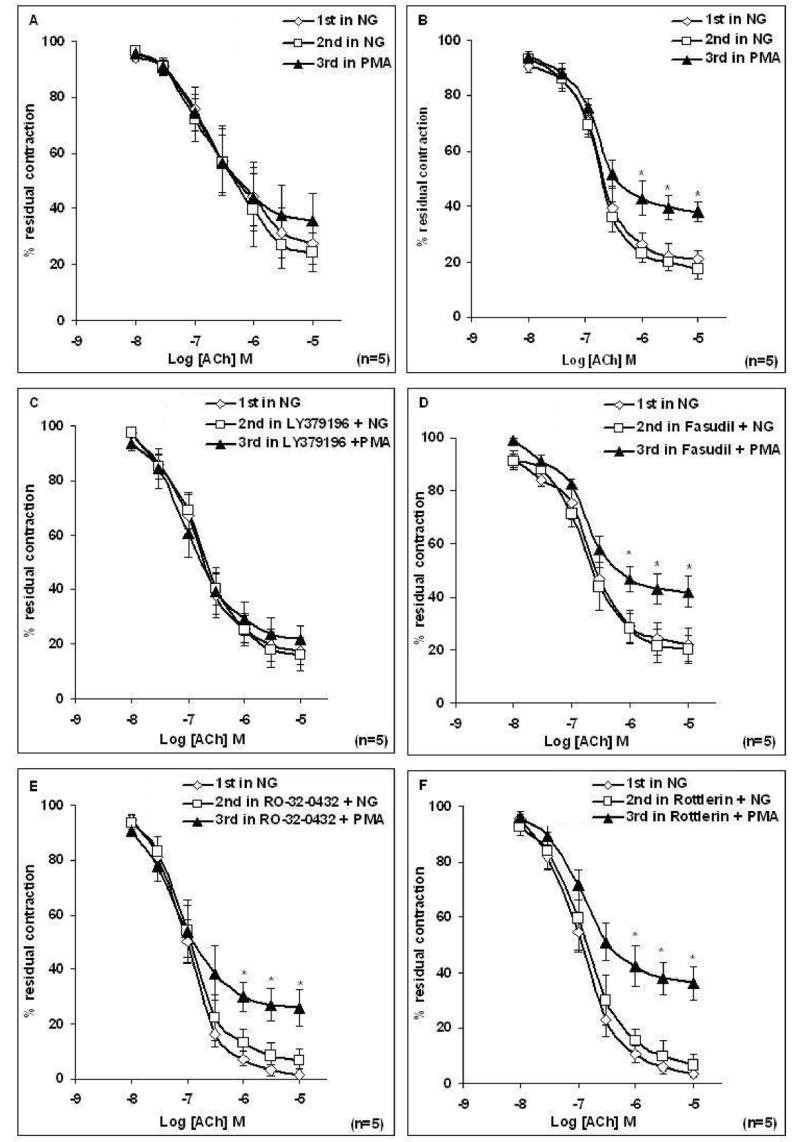
(A–B) Rings were incubated with Krebs containing normal glucose (NG, 6mM) and/or Krebs containing PMA (0.1 μM) for 3 h before concentration response curve (CRC) to ACh was determined. Treatment of aortic rings with PMA for 3 h caused a significant reduction in maximal relaxation to ACh in females. (C–F) Rings from female rats were incubated with Krebs containing NG or Krebs containing LY379196 (1 μM), Fasudil (1μM), Ro-32-0432 (9 nM), or Rottlerin (6 μM) for 20 min or Krebs containing LY379196, Fasudil, Ro-32-0432 or Rottlerin and PMA (0.1 μM) for 3 h before the CRC to ACh was determined. Treatment of aorta with LY379196, but not Fasudil, Ro-32-0432 or Rottlerin prior to PMA restored the abnormal ACh relaxation of aorta. Data are presented as the mean ± S.EM. (*P < 0.05 paired t-test).
