Abstract
The uptake and modification of exogenous phosphatidylcholine (PC) by several Mycoplasma and Spiroplasma species was investigated. While in most Mycoplasma species and in all Spiroplasma species tested the PC appears to be incorporated unchanged from the growth medium, the PC of M. gallisepticum, M. pulmonis, and M. pneumoniae was disaturated PC, apparently formed by modification of 1-saturated-2-unsaturated PC from the growth medium. The modification of the exogenous PC by M. gallisepticum was inhibited by chloramphenicol under conditions that did not affect de novo synthesis of phosphatidylglycerol. A low activity of an endogenous phospholipase A was detected in native M. gallisepticum membranes. The activity was markedly stimulated by treating the membranes with low concentrations of the nonionic detergents. The PC modification was affected by the fatty acid composition of the exogenous PC species. Diunsaturated, 1-saturated-2-unsaturated, and 1-unsaturated-2-saturated PCs were modified to various extents, whereas the disaturated dipalmitoyl PC (DPPC) was not. Both modified and unmodified PCs were incorporated by the cells, but the unmodified DPPC was incorporated at a lower rate and to a lesser extent. The possibility that the incorporation of DPPC into M. gallisepticum cells is associated with the formation of intracytoplasmic membranes is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clejan S., Bittman R., Rottem S. Uptake, transbilayer distribution, and movement of cholesterol in growing Mycoplasma capricolum cells. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4579–4583. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullis P. R., de Kruijff B. Lipid polymorphism and the functional roles of lipids in biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 20;559(4):399–420. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. J., Katznel A., Razin S., Rottem S. Spiroplasma membrane lipids. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):118–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.118-122.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrati H., Rottem S., Razin S. Lipid and protein membrane components associated with cholesterol uptake by Mycoplasmas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Mar 6;641(2):386–394. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90494-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatt S., Morag B., Rottem S. Lysophospholipase-catalyzed hydrolysis of lysophospholipids in Mycoplasma gallisepticum membranes. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1095–1101. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1095-1101.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine H. Bacterial membranes and lipid packing theory. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 15;25(13):1501–1507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross Z., Rottem S., Bittman R. Phospholipid interconversions in Mycoplasma capricolum. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Feb;122(1):169–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane I., Razin S. Synthesis and turnover of membrane protein and lipid in Mycoplasma laidlawii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 3;183(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent C., Lennarz W. J. An osmotically fragile mutant of Bacillus subtilis with an active membrane-associated phospholipase A 1 . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2793–2797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchhoff H., Rosengarten R., Lotz W., Fischer M., Lopatta D. Flask-shaped mycoplasmas: properties and pathogenicity for man and animals. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 Sep;20(9):848–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuypers F. A., Roelofsen B., Op den Kamp J. A., Van Deenen L. L. The membrane of intact human erythrocytes tolerates only limited changes in the fatty acid composition of its phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 25;769(2):337–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90315-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plackett P. The glycerolipids of Mycoplasma mycoides. Biochemistry. 1967 Sep;6(9):2746–2754. doi: 10.1021/bi00861a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Kutner S., Efrati H., Rottem S. Phospholipid and cholesterol uptake by Mycoplasma cells and membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 6;598(3):628–640. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. The mycoplasmas. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):414–470. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.414-470.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
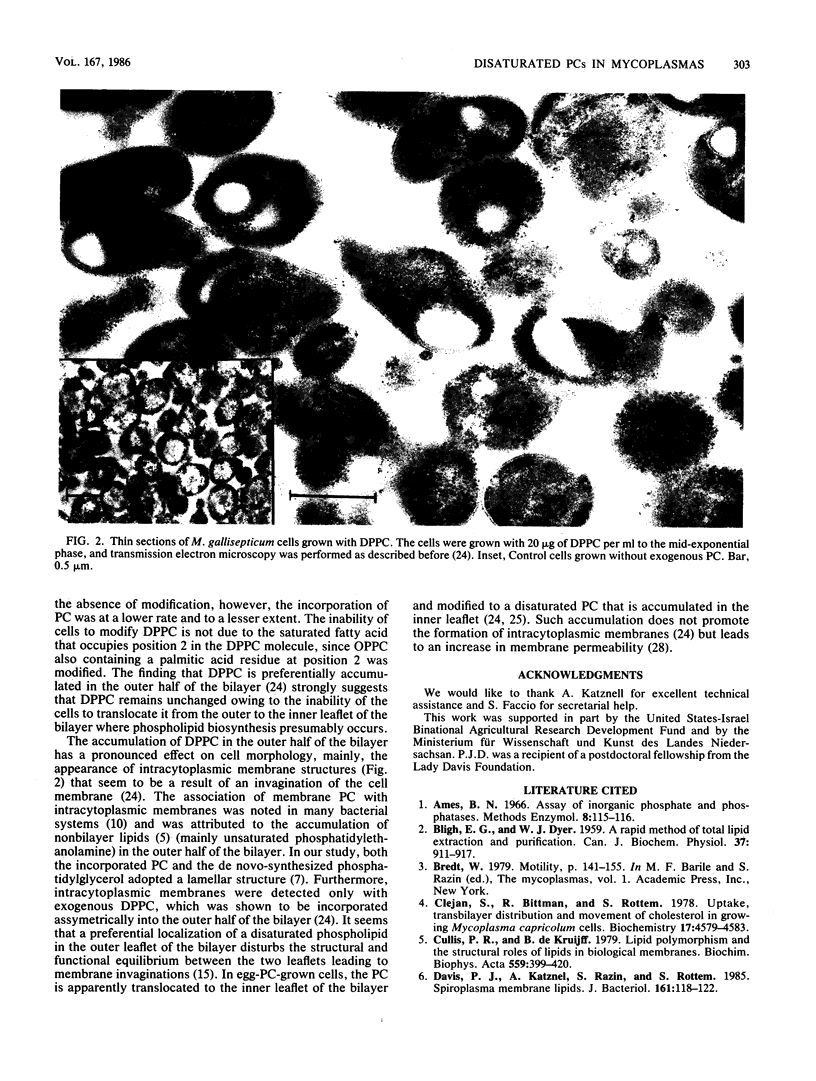
- Rottem S., Davis P. J., Gross Z., Ne'eman Z. Uptake and transbilayer distribution of phosphatidylcholines in Mycoplasma gallisepticum and their effect on cell morphology. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 Sep;20(9):812–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Markowitz O. Membrane lipids of Mycoplasma gallisepticum: a disaturated phosphatidylcholine and a phosphatidylglycerol with an unusual positional distribution of fatty acids. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 10;18(14):2930–2935. doi: 10.1021/bi00581a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S. Membrane lipids of mycoplasmas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 27;604(1):65–90. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90585-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Razin S. Membrane lipids of Mycoplasma hominis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):565–571. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.565-571.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Shirvan M. H., Gross Z. Phase separation, ion permeability, and the isolation of membranes from osmotically stable mycoplasmas. Yale J Biol Med. 1983 Sep-Dec;56(5-6):405–411. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Verkleij A. J. Possible association of segregated lipid domains of Mycoplasma gallisepticum membranes with cell resistance to osmotic lysis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):338–345. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.338-345.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F. Nutritional requirements of PPLO and their relation to metabolic function. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 15;79:508–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Golde L. M., McElhaney R. N., van Deenen L. L. A membrane-bound lysophospholipase from Mycoplasma laidlawii strain B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 2;231(1):245–249. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90275-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]