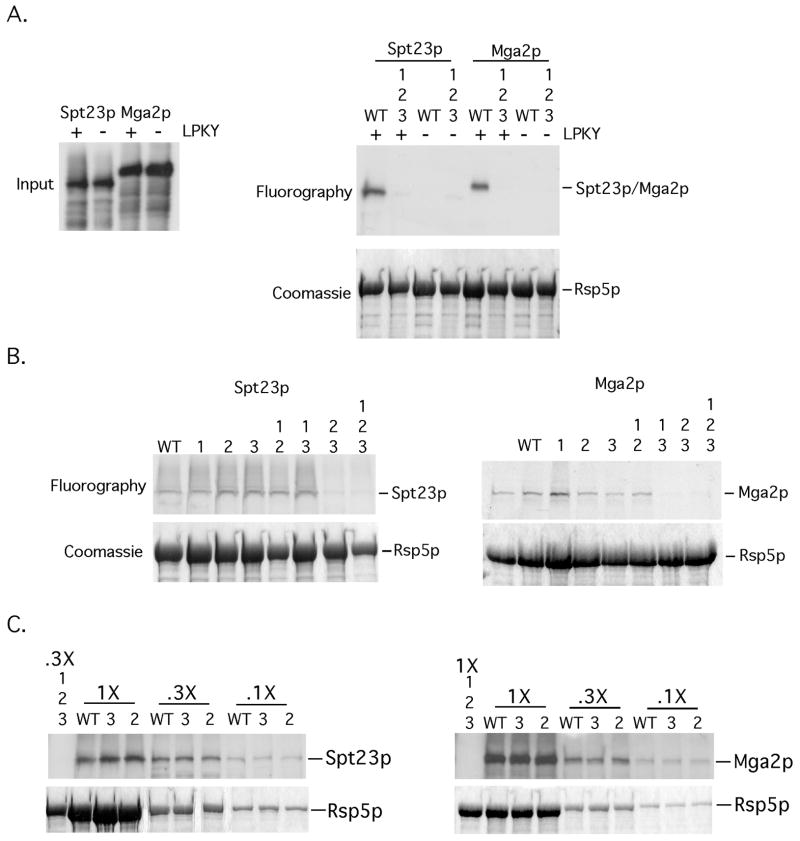
FIG 1. Mutations in WW domains 2 and 3 of Rsp5p abrogate an interaction with Spt23p and Mga2p in vitro.
(A) (left panel) Inputs of in vitro translated 35S-labeled Spt23p, Spt23pΔLPKY, Mga2p and Mga2ΔLPKY used for the in vitro binding experiments are depicted. (right panel) Equivalent amounts of bead-bound recombinant WT GST-Rsp5p or GST-Rsp5p harboring mutations in all three WW domains were incubated with equal amounts of in vitro translated material. Protein complexes were allowed to form, followed by centrifugation and washing of bead-bound material. Pelleted material was resuspended in loading buffer, resolved by SDS-PAGE and the amount of radiolabeled protein was determined by fluorography. The gel was rehydrated and stained with Coomassie Blue to show equal amounts of Rsp5p in the pelleted material. (B) The above-described binding assays were performed with the designated WW domain mutants and 35S-labeled Spt23p or Mga2p. (C) Binding assays were also performed with varying amounts of WT Rsp5p or Rsp5p mutants (WW2 and WW3) and 35S-labeled Spt23p or Mga2p.