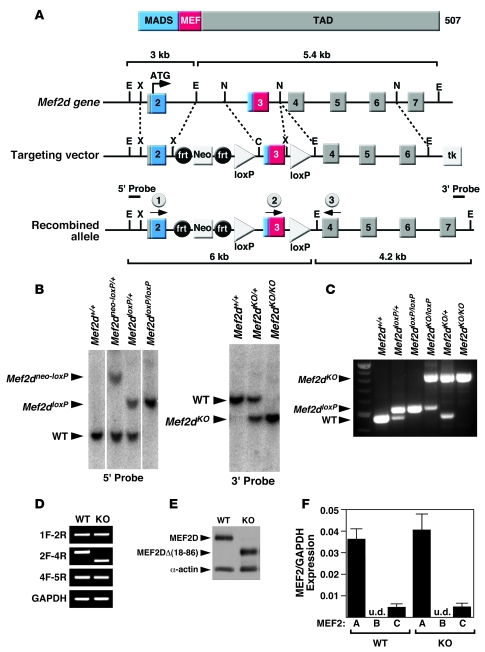
Figure 1. Generation of mice with a conditional Mef2d mutation.
(A) Schematic representation of the mouse Mef2d locus and targeting strategy. Positions of 3ι and 5ι probes used for Southern blots are shown. The positions of the PCR primers used for genotyping mutant alleles are marked with arrows (circles labeled 1, 2, and 3). C, ClaI; frt, FLP recombinase target; E, EcoRI; TAD, transactivation domain; MADS, MCM1, agamous, deficiens, serum response factor; N, NcoI; X, XhoI. (B) Southern blot analysis of Mef2d mutant alleles. Genomic DNA was digested with EcoRI and hybridized to a 5ι probe in the left panel and to a 3ι probe in the right panel. WT, wild-type allele; Mef2dneo-loxP, conditional allele; Mef2dloxP, conditional allele with the Neo cassette removed; Mef2dKO, null allele. (C) PCR genotyping to distinguish different Mef2d alleles. The positions of the primers that produce these PCR products are labeled (1, 2, and 3) and circled on A. All 3 primers were added to the PCR reactions and the PCR products were loaded into lanes 2–7. (D) Expression of wild-type and mutant Mef2d detected by RT-PCR. Mef2d mutant allele lacks exon 3, which encodes the MADS- and MEF2-specific domains. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Labels on the left side of the panel indicate exon location and direction of primers used for RT-PCR. (E) Western blot analysis to detect WT and mutant MEF2D (KO) proteins. The mutant MEF2D protein is truncated due to deletion of exon 3. α-Actin protein was used as a loading control. (F) Expression level of Mef2 detected by quantitative PCR. Error bars indicate ±SEM. u.d., undetectable.