Abstract
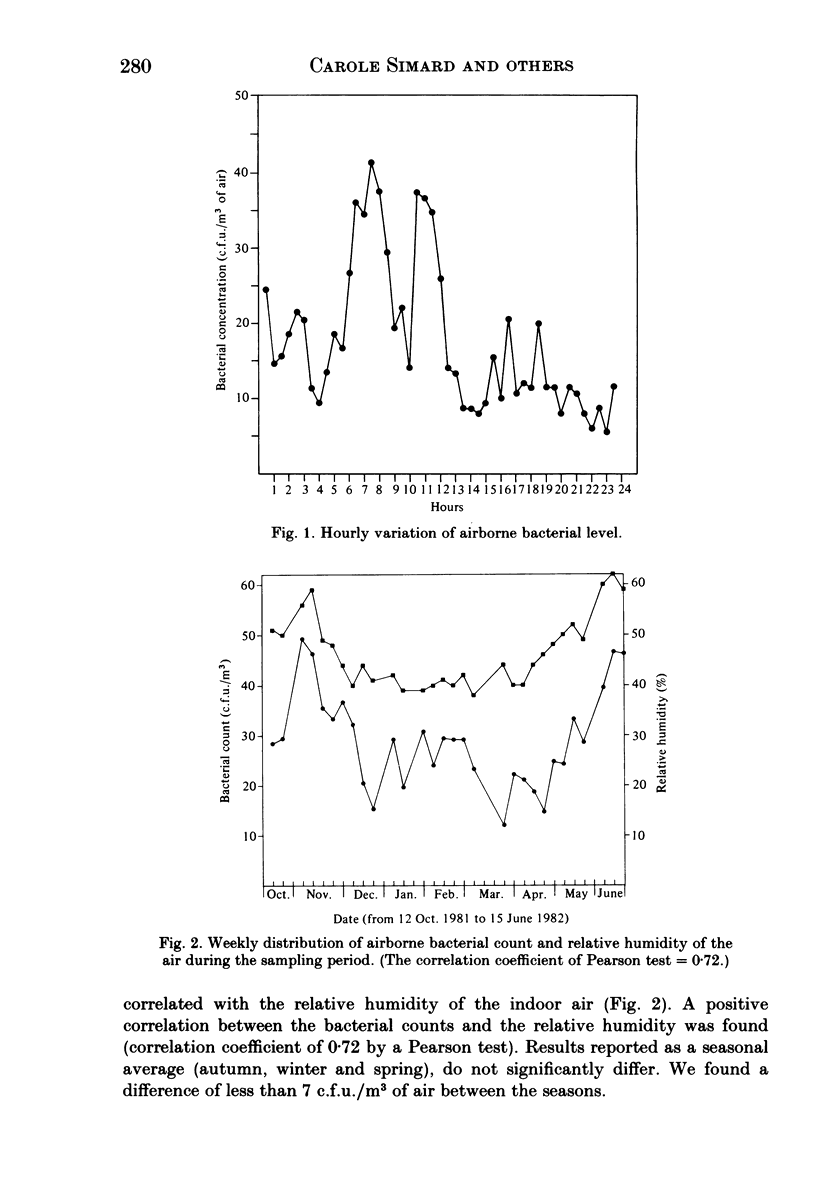
The microbial and viral flora in the ventilating ducts of an apartment building was evaluated. Several types of sampler (slit sampler, Andersen sampler, large volume air sampler) were used to evaluate the hourly, weekly and seasonal variation of this flora. The mean bacterial concentration was 17.2 e.f.u./m3 with a maximum level at 07.30 h (41.3 c.f.u./m3) and a minimal concentration in the early afternoon (8 c.f.u./m3). The bacterial concentration observed correlated with the relative humidity in the air-ducts although there were no seasonal differences. The bacteria were mainly gram-positive cocci (73.5%) represented by a large number of Micrococcaceae (47.1%); gram-positive bacilli accounted for 14.2% of the isolates, gram-negative bacilli 12.0% and gram-negative cocci 0.3%. The majority of the bacteria-carrying particles were in the respirable range with 80.4% of them being less than 5 microns. The methods used did not result in the isolation of viruses during the winter sampling period.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN A. A. New sampler for the collection, sizing, and enumeration of viable airborne particles. J Bacteriol. 1958 Nov;76(5):471–484. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.5.471-484.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couch R. B. Viruses and indoor air pollution. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1981 Dec;57(10):907–921. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favero M. S., Puleo J. R., Marshall J. H., Oxborrow G. S. Comparative levels and types of microbial contamination detected in industrial clean rooms. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Jul;14(4):539–551. doi: 10.1128/am.14.4.539-551.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. E., Prince J., Hawksworth M. A bacteriological survey of the domestic environment. J Appl Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;45(3):357–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1978.tb04236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENE V. W., VESLEY D., BOND R. G., MICHAELSEN G. S. Microbiological contamination of hospital air. II. Qualitative studies. Appl Microbiol. 1962 Nov;10:567–571. doi: 10.1128/am.10.6.567-571.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerba C. P., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Microbiological hazards of household toilets: droplet production and the fate of residual organisms. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):229–237. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.229-237.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HATCH T. F. Distribution and deposition of inhaled particles in respiratory tract. Bacteriol Rev. 1961 Sep;25:237–240. doi: 10.1128/br.25.3.237-240.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRCH A. Bacterial contamination of the air in boot and shoe factories. Br J Ind Med. 1951 Jan;8(1):8–11. doi: 10.1136/oem.8.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRCH A., LIDWELL O. M., WILLIAMS R. E. The bacterial flora of the air of occupied rooms. J Hyg (Lond) 1956 Dec;54(4):512–523. doi: 10.1017/s002217240004479x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle L. E., Jr, Murray S. H. The importance of the quality of indoor air. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1981 Dec;57(10):827–844. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houk V. N. Spread of tuberculosis via recirculated air in a naval vessel: the Byrd study. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;353:10–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb18901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight V. Viruses as agents of airborne contagion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;353:147–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb18917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGMUIR A. D. Epidemiology of airborne infection. Bacteriol Rev. 1961 Sep;25:173–181. doi: 10.1128/br.25.3.173-181.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidwell O. M., Noble W. C. A modification of the Andersen sampler for use in occupied environments. J Appl Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;28(2):280–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1965.tb02154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAY K. R. CALIBRATION OF A MODIFIED ANDERSEN BACTERIAL AEROSOL SAMPLER. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jan;12:37–43. doi: 10.1128/am.12.1.37-43.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moschandreas D. J. Exposure to pollutants and daily time budgets of people. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1981 Dec;57(10):845–859. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOBLE W. C., LIDWELL O. M., KINGSTON D. THE SIZE DISTRIBUTION OF AIRBORNE PARTICLES CARRYING MICRO-ORGANISMS. J Hyg (Lond) 1963 Dec;61:385–391. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400020994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S., Stern A. C. A Study of Air Pollution in New York City. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1937 Apr;27(4):321–333. doi: 10.2105/ajph.27.4.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley R. L. Indoor spread of respiratory infection by recirculation of air. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1979 Sep-Oct;15(5):699–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott E., Bloomfield S. F., Barlow C. G. An investigation of microbial contamination in the home. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Oct;89(2):279–293. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells W. F., Zappasodi P. THE EFFECT OF HUMIDITY ON BETA STREPTOCOCCI (GROUP C) ATOMIZED INTO AIR. Science. 1942 Sep 18;96(2490):277–278. doi: 10.1126/science.96.2490.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White L. A., Hadley D. J., Davids D. E., Naylor R. Improved large-volume sampler for the collection of bacterial cells from aerosol. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Mar;29(3):335–339. doi: 10.1128/am.29.3.335-339.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



