Abstract
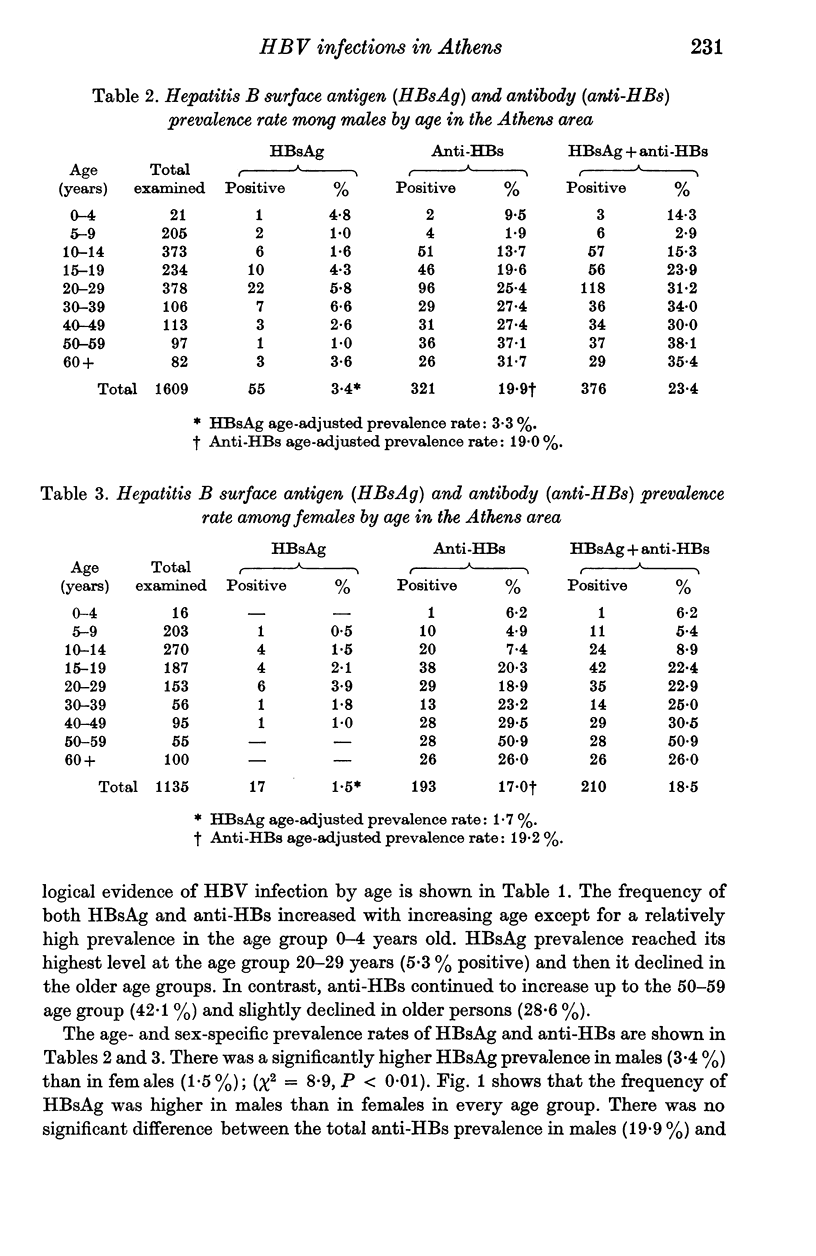
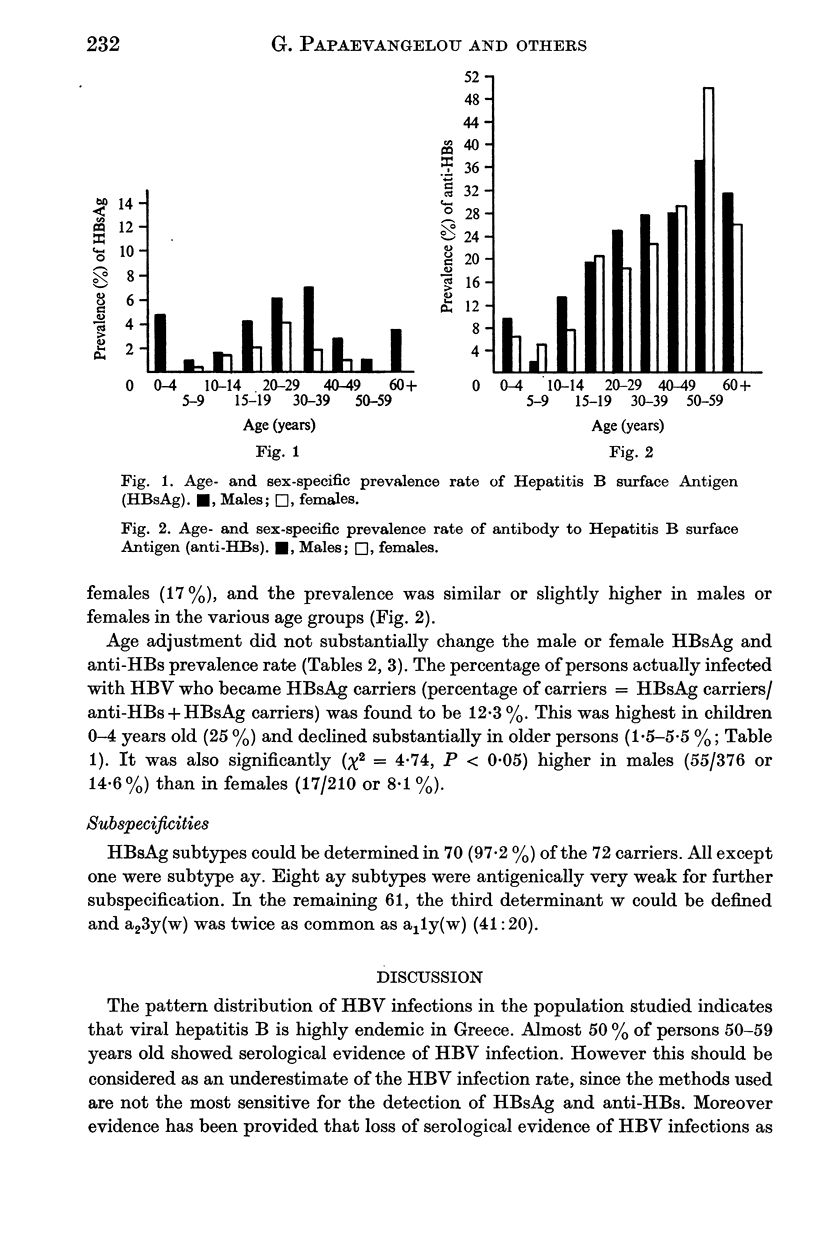
A seroepidemiological survey of a sample-roughly representative by age and sex - of 2744 persons of the Greater Athens area revealed that hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections are highly endemic in Greece. Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) was detected in 72(2-6%) of them. The subtype was identified in 70 of the 72 carriers, and 69 were ay; the other was ad. Determinant w was present in all 61 that were capable of being typed further, and a23y(w) was twice as common as a11y(w). Antibody to HBsAg (anti-HBs) was found in 514 (18-7%) persons. The prevalence of the HBsAg rose rapidly with age, reaching peak values (5-3%) at 20-29 years, while anti-HBs reached its highest value (42-1%) in older age groups (50-59 years). The frequency of HBsAg was significantly higher in males (3-4%) than in females (1-5%). The percentage of infected persons who become chronic HBsAg carriers (12-3%) was found higher than in other developed populations. It was also found higher in children (25%) than in adults (5-5%) and in males (14-6%) than in females (8-1%). These data indicate that HBV infection in early life is a major risk factor in the development of HBsAg carriers and support the hypothesis that males are more likely to become HBsAg carriers than females.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumberg B. S., Sutnick A. I., London W. T., Melartin L. Sex distribution of Australia antigen. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Aug;130(2):227–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherubin C. E., Purcell R. H., Lander J. J., McGinn T. G., Cone L. A. Acquisition of antibody to hepatitis B antigen in three socioeconomically different medical populations. Lancet. 1972 Jul 22;2(7769):149–151. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91325-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerety R. J., Hoofnagle J. H., Markenson J. A., Barker L. F. Exposure to hepatitis B virus and development of the chronic HBAg carrier state in children. J Pediatr. 1974 May;84(5):661–665. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman R. A., Benenson M. W., Scott R. M., Snitbhan R., Top F. H., Jr, Pantuwatana S. An epidemiologic study of hepatitis B virus in Bangkok, Thailand. Am J Epidemiol. 1975 Feb;101(2):144–159. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadziyannis S. J. Chronic viral hepatitis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1974 May;3(2):391–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krugman S., Giles J. P. Viral hepatitis, type B (MS-2-strain). Further observations on natural history and prevention. N Engl J Med. 1973 Apr 12;288(15):755–760. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197304122881503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bouvier G. L., McCollum R. W. Australia (hepatitis-associated) antigen: physicochemical and immunological characteristics. Adv Virus Res. 1970;16:357–396. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60027-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bouvier G. L. The heterogeneity of Australia antigen. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jun;123(6):671–675. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.6.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzur S., Burgert S., Blumberg B. S. Geographical distribution of Australia antigen determinants d, y and w. Nature. 1974 Jan 4;247(5435):38–40. doi: 10.1038/247038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley J. W., Edwards V. M., Meihaus J. E., Redeker A. G. Subdeterminants d and y of hepatitis B antigen as epidemiologic markers. Am J Epidemiol. 1972 Jun;95(6):529–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesendorfer F., Krassnitzky O., Wewalka F. Immunelektrophoretischer Nachweis von "Hepatitis-Associated-Antigen" (Au-SH-Antigen. Klin Wochenschr. 1970 Jan 1;48(1):58–59. doi: 10.1007/BF01486135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock S., Fox R. A., Niazi S. P., Scheuer P. J. Chronic liver disease and primary liver-cell cancer with hepatitis-associated (Australia) antigen in serum. Lancet. 1970 Jun 13;1(7659):1243–1247. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91737-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmuness W., Hirsch R. L., Prince A. M., Levine R. W., Harley E. J., Ikram H. Hepatitis B surface antigen in blood donors: further observations. J Infect Dis. 1975 Feb;131(2):111–118. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.2.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmuness W., Prince A. M., Diebolt G., Leblanc L., Baylet R., Masseyeff R., Linhard J. The epidemiology of hepatitis B infections in Africa: results of a pilot survey in the Republic of Senegal. Am J Epidemiol. 1973 Aug;98(2):104–110. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vissoulis C. H., Papaevangelou G. Prevalence of hepatitis B antigen. J Infect Dis. 1973 Dec;128(6):807–807. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.6.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


