Abstract
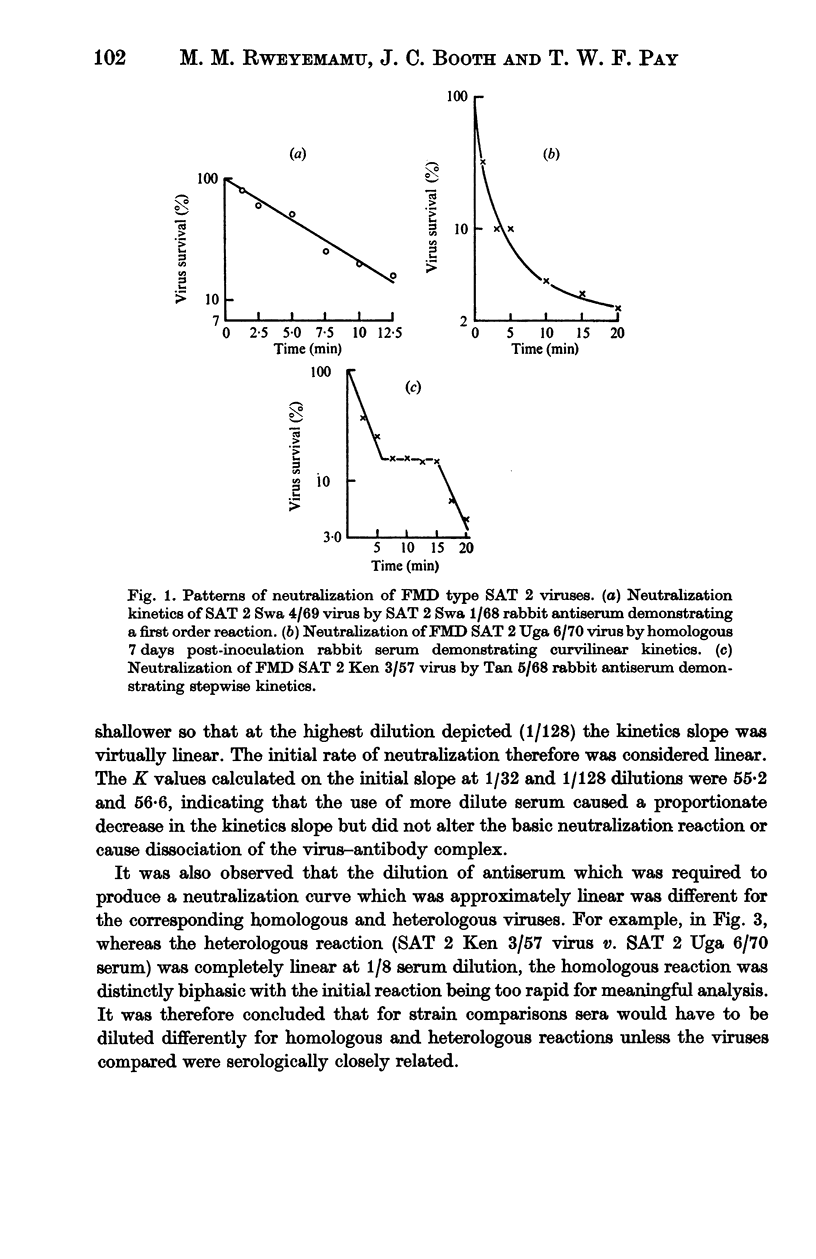
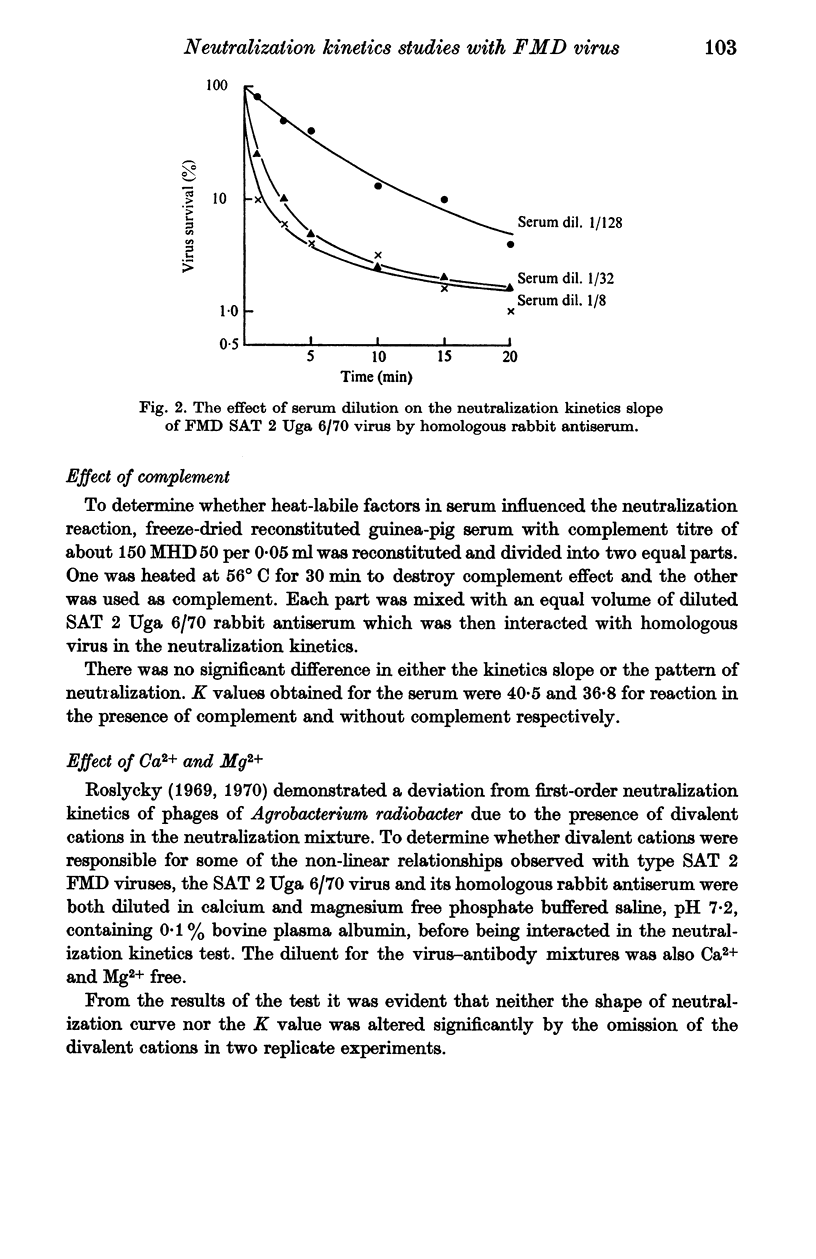
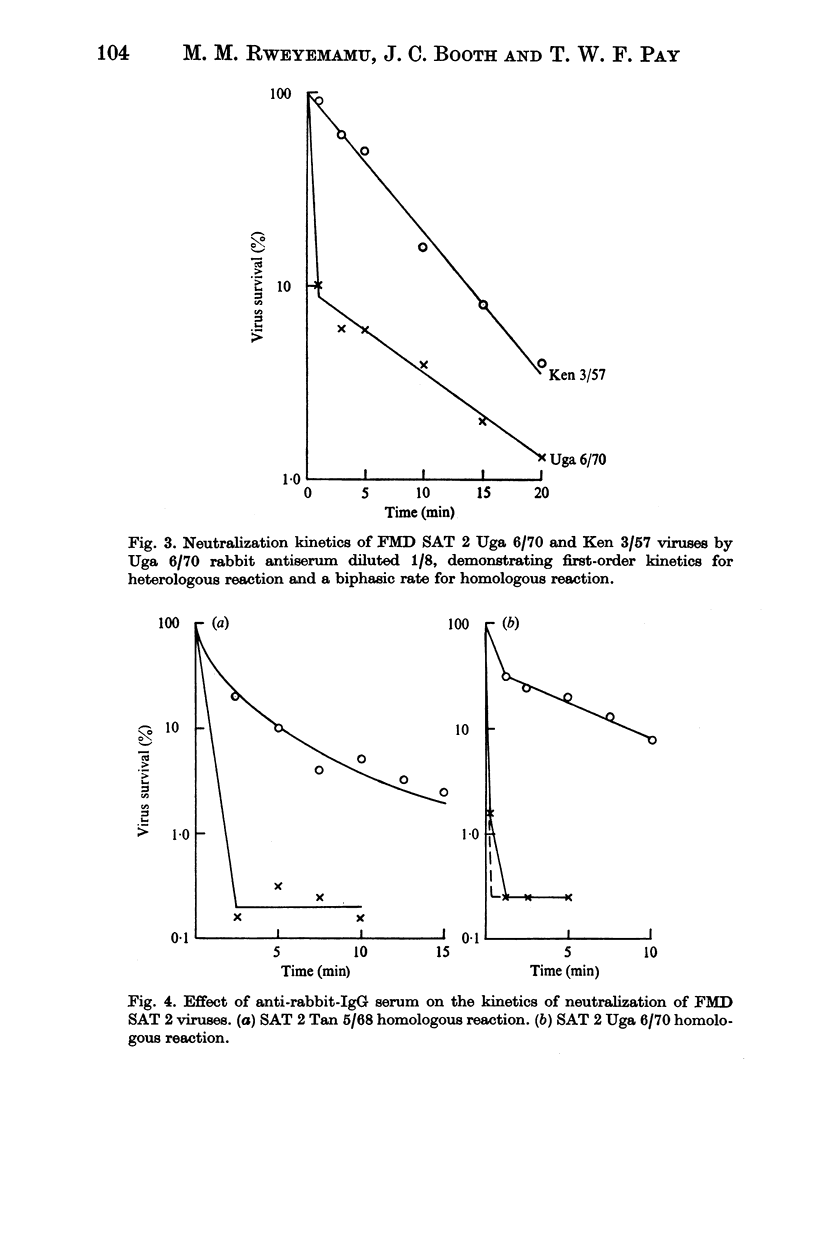
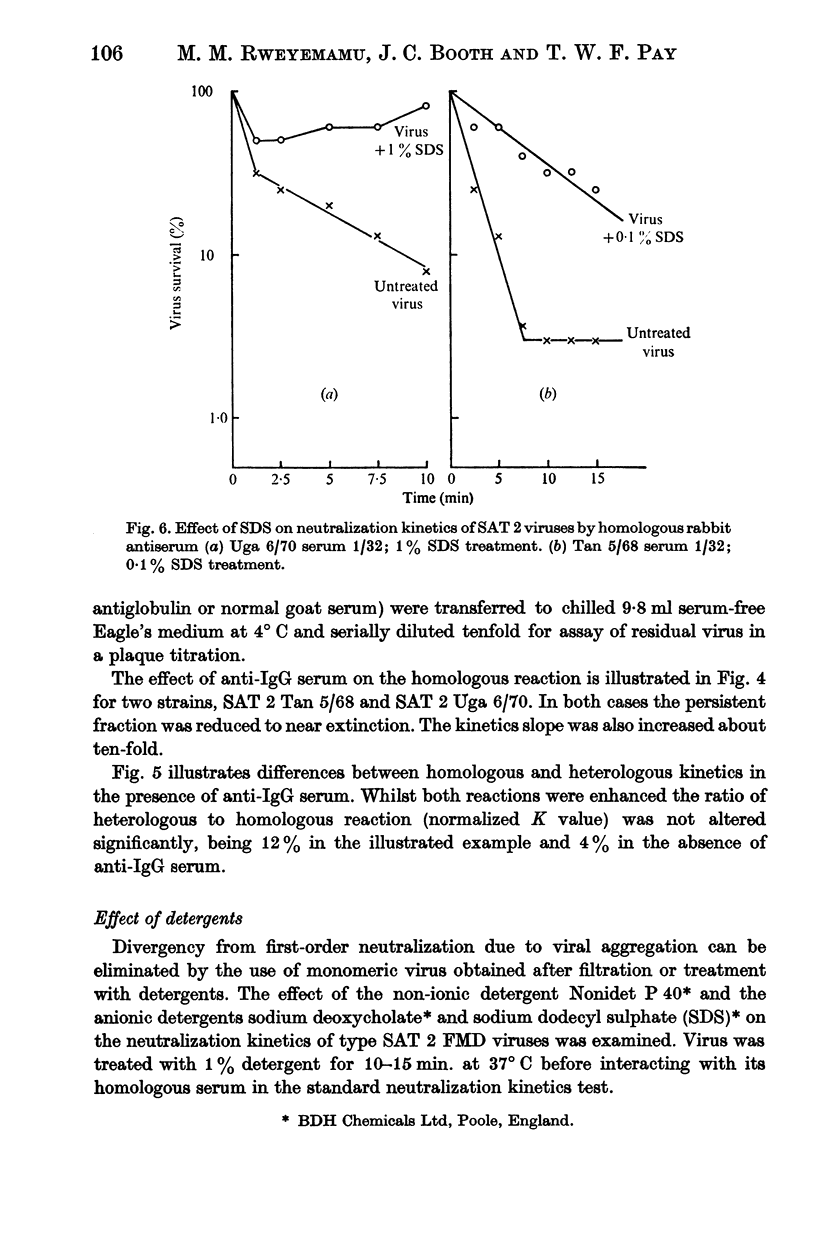
A study of the kinetics of inactivation of foot-and-mouth disease virus type SAT 2 strains revealed that in most cases the rate of neutralization was not rectilinear. Deviations from first-order kinetics observed represented biphasic or parabolic and stepwise reactions. The initial rate was rapid and showed no lag phase or shoulder. The effects of deviations from linearity could be minimized by dilution of antiserum to a suitable extent. Treatment of virus-antibody mixtures with anti-species globulin resulted in enhancement of the rate of neutralization of homologous and heterologous reactions without significantly altering the relation between the two. This treatment also considerably reduced the amount of the persistent fraction. In attempt to disaggregate virus it was observed that sodium dodecyl sulphate inhibited neutralization of virus by specific antiserum.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHE W. K., SCHERP H. W. ANTIGENIC ANALYSIS OF HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS BY NEUTRALIZATION KINETICS. J Immunol. 1963 Nov;91:658–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashe W. K., Notkins A. L. Neutralization of an infectious herpes simplex virus-antibody complex by anti-gamma-globulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):447–451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADISH C. J., FARLEY J. O., FERRIER H. E. Studies on the nature of the nature of the neutralization reaction and the competition for neutralizing antibody between components of the virus system of foot-and-mouth disease. Virology. 1962 Nov;18:378–400. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN F., CARTWRIGHT B. PURIFICATION OF RADIOACTIVE FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS. Nature. 1963 Sep 21;199:1168–1170. doi: 10.1038/1991168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buening G. M., Gratzek J. B. Comparison of selected characteristics of four strains of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. Am J Vet Res. 1967 Sep;28(126):1257–1267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAPSTICK P. B., SELLERS R. F., STEWART C. L. The neutralisation of the virus of the foot-and-mouth disease by immune serum. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1960;9:606–620. doi: 10.1007/BF01242147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho C. T., Feng K. K. Non-immunological precipitation of serum by sodium dodecyl sulfate in agar diffusion. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):557–560. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.557-560.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cihak J. Neutralization of infectious ME (Maus-Elberfeld) virus-antibody complexes by anti-gamma-globulin antibody. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Sep 26;159(1):73–82. doi: 10.1007/BF02122651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney M. K., Kenny G. E., Tam R., Fox J. P. Cross relationships among 37 rhinoviruses demonstrated by virus neutralization with potent monotypic rabbit antisera. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):335–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.335-340.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M., STRICKLAND A. G. A study of the basic aspects of neutralization of two animal viruses, western equine encephalitis virus and poliomyelitis virus. Virology. 1956 Apr;2(2):162–205. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(56)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. O., Neurath H. THE SEROLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF DENATURED ANTIBODIES. Science. 1943 Sep 24;98(2543):284–285. doi: 10.1126/science.98.2543.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman A. J. A comparison of some immunological methods for the differentiation of strains of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Apr;74(2):215–225. doi: 10.1017/s002217240002427x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwaltney J. M., Jr, Calhoun A. M. Viral aggregation resulting in the failure to correctly identify an unknown rhinovirus. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Sep;20(3):390–392. doi: 10.1128/am.20.3.390-392.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASHIMOTO N., PRINCE A. M. Kinetic studies on the neutralization reaction between Japanese encephalitis virus and antiserum. Virology. 1963 Mar;19:261–272. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90063-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahon N. The kinetics of neutralization of Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus by antiserum and the reversibility of the reaction. J Gen Virol. 1969 Jan;4(1):77–88. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-4-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haimovich J., Sela M. Inactivation of bacteriophage T4, of poly-D-alanyl bacteriophage and of penicilloyl bacteriophage by immunospecifically isolated IgM and IgG antibodies. J Immunol. 1969 Jul;103(1):45–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heineman H. S. Herpes simplex neutralizing antibody--quantitation of the complement-dependent fraction in different phases of adult human infection. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):214–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAFFERTY K. J. THE INTERACTION BETWEEN VIRUS AND ANTIBODY. I. KINETIC STUDIES. Virology. 1963 Sep;21:61–75. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDEL B. Reversibility of the reaction between polio-virus and neutralizing antibody of rabbit origin. Virology. 1961 Jul;14:316–328. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90317-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOWAT G. N., CHAPMAN W. G. Growth of foot-and-mouth disease virus in a fibroblastic cell line derived from hamster kidneys. Nature. 1962 Apr 21;194:253–255. doi: 10.1038/194253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinsen J. S. Two-plaque-size variants of foot-and-mouth disease virus differing in neutralization by guinea-pig antisera. Res Vet Sci. 1971 Jul;12(4):399–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBRIDE W. D. Antigenic analysis of polioviruses by kinetic studies of serum neutralization. Virology. 1959 Jan;7(1):45–58. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OZAKI Y., DIWAN A. R., McBRIDE W. D., MELNICK J. L. Antigenic characterization of oral poliovaccine progeny by neutralization kinetics. J Immunol. 1963 Feb;90:288–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer E. L., Martin M. L., Hierholzer J. C., Ziegler D. W. Nonspecific precipitation of serum proteins by sodium lauryl sulfate in agar diffusion and immunoelectrophoresis. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):903–906. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.903-906.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillipson L. Interaction between poliovirus and immunoglobulins. II. Basic aspects of virus-antibody interaction. Virology. 1966 Jan;28(1):35–46. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90304-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potgieter L. N., Maré C. J. Differentiation of strains of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus by neutralization kinetics with late 19S rabbit antibodies. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):520–527. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.520-527.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roslycky E. B. Anomaly in the neutralization kinetics of phages of Agrobacterium radiobacter. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Sep;15(9):1033–1042. doi: 10.1139/m69-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roslycky E. B. Radiobacterphage neutralization anomaly in relation to cations. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Jun;16(6):527–533. doi: 10.1139/m70-089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takabayashi K., McIntosh K. Effect of heat-labile factors on the neutralization of vaccinia virus by human. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):582–589. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.582-589.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Virus aggregation as the cause of the non-neutralizable persistent fraction. J Virol. 1967 Jun;1(3):478–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.3.478-488.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler C. E., Jr, Briggaman R. A., Henderson R. R. Discrimination between two strains (types) of Herpes simplex virus by various modifications of the neutralization test. J Immunol. 1969 May;102(5):1179–1192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


