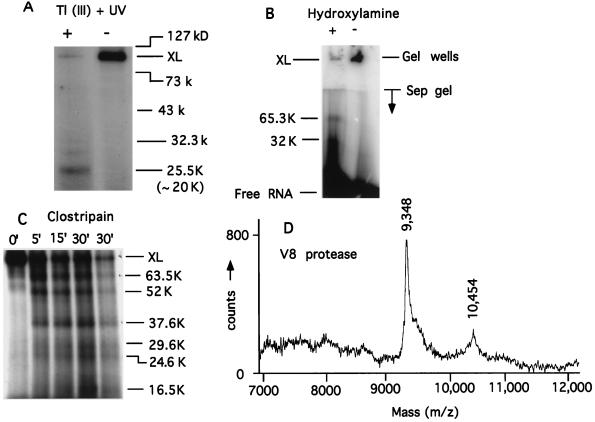
Figure 6.
Mapping the RNA-binding site. (A) Ten percent acrylamide-SDS Tris-Gly gel. Cleavage with thallium acetate + 254 nm of UV irradiation). Tl (III) OAc (100 mM) was added to cross-linked T7 RNAP and irradiated with 254 nm of UV light for 5 min. The size range of the markers is indicated while the actual (minus the mass of BP-RNA) mass of the proteolytic fragment is given in parentheses. (B) Cleavage with hydroxylamine. Ten percent acrylamide-SDS Tris-Gly gel. Purified cross-link was dissolved in 0.1 M K2CO3 (pH 10) and the cleavage was done as in ref. 37. To compensate for the lability of the P-N bond in the cross-link at pH 10, 37°C (where the NH2 OH-cleavage reaction occurred), we had to use 6- to 8-fold cross-linked T7 RNAP in the + lane to see the cleaved fragments. In lane − the cross-link ran near the gel well. The actual (i.e., minus the mass of BP-RNA) mass of the proteolytic fragments is given. Protein markers (not shown) were the same as in A. (C) Ten percent acrylamide-SDS Tris-Tricine gel. Cleavage with clostripain was carried out as specified by the manufacturer (Promega) at cross-link to protease mass ratio of 100:1. The actual (minus the mass of BP-RNA) mass of the proteolytic fragments is given. To better visualize the bands, less material was loaded in the last lane (30′) compared with the others. Protein markers (not shown) were the same as in A. (D) Cleavage with V8 protease in gel pieces was carried out according to the manufacturer (Promega) at cross-link to protease mass ratio of 10:1. The plot shows a trace of the mass spectrogram in the relevant mass range.