Abstract
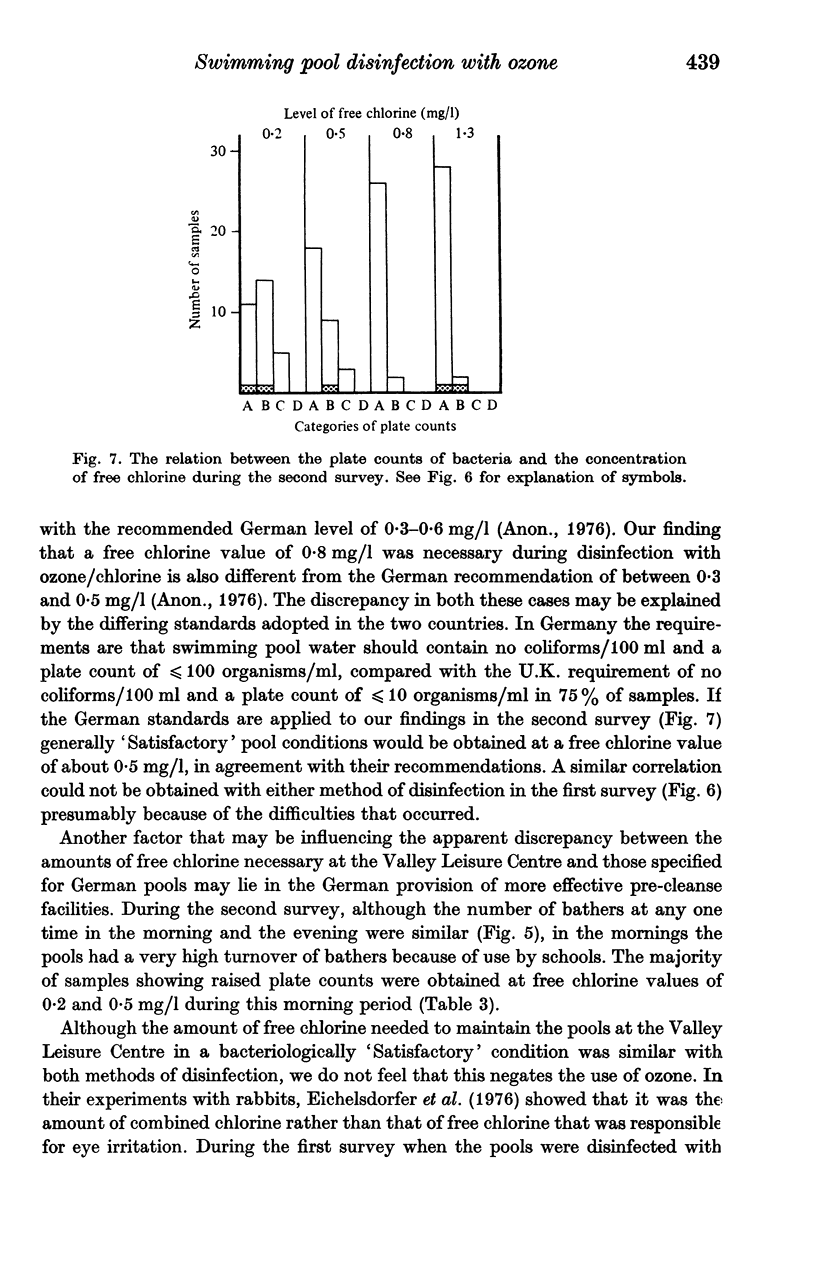
A bacteriological study was carried out on the first Leisure Centre swimming pools in the United Kingdom to be disinfected with ozone/chlorine. Results suggested that a free chlorine concentration of approximately 0.8 mg/l was necessary to maintain the pools in a bacteriologically satisfactory condition. This amount of free chlorine was similar to that required when the pool was disinfected with chlorine alone. However, the associated amount of combined chlorine was much lower when disinfection was by ozone/chlorine and this gave more acceptable bathing conditions. Implications for the manamgement of pools disinfected by this method are discussed.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black A. P., Keirn M. A., Smith J. J., Jr, Dykes G. M., Jr, Harlan W. E. The disinfection of swimming pool water. II. A field study of the disinfection of public swimming pools. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1970 Apr;60(4):740–750. doi: 10.2105/ajph.60.4.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


