Figure 2.
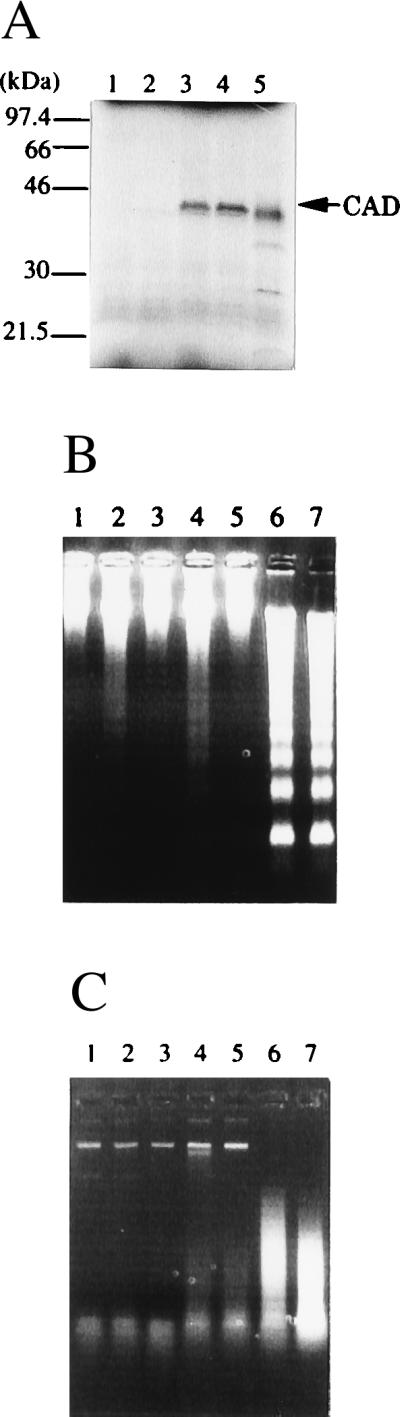
Expression of human CAD in a cell-free system. (A) Synthesis of human CAD protein in reticulocyte lysates. The pBS-hCAD carrying human CAD cDNA under the T7 promoter (lanes 3 and 4), pcDNA-CAD carrying mouse CAD under the T7 promoter (lane 5), or empty vector (lanes 1 and 2) was subjected to in vitro transcription and translation in the presence of [35S]Met in a final volume of 50 μl. The reaction mixtures in lanes 2, 4, and 5 included 160 ng of glutathione S-transferase–mouse ICAD-L. After the reaction, 8-μl aliquots were analyzed by electrophoresis on a 10–20% gradient polyacrylamide gel, followed by autoradiography. Molecular masses of the standard proteins are shown in kDa. (B and C) The activity of the human CAD synthesized in reticulocyte lysates. Human CAD (lanes 3–6) or mouse CAD (lane 7) was synthesized in the in vitro transcription and translation system in a final volume of 50 μl in the absence (lanes 3 and 4) or presence (lanes 5–7) of 160 ng of glutathione S-transferase–mouse ICAD-L. Using 3-μl aliquots, the CAD activity with nuclei (B) or plasmid DNA (C) was determined in the absence (lanes 3 and 5) or presence (lanes 4, 6, and 7) of 90 ng of caspase 3. The empty vector (pBluescript) (lanes 1 and 2) was subjected to a similar procedure in the absence (lane 1) or presence (lane 2) of caspase 3.
