Abstract
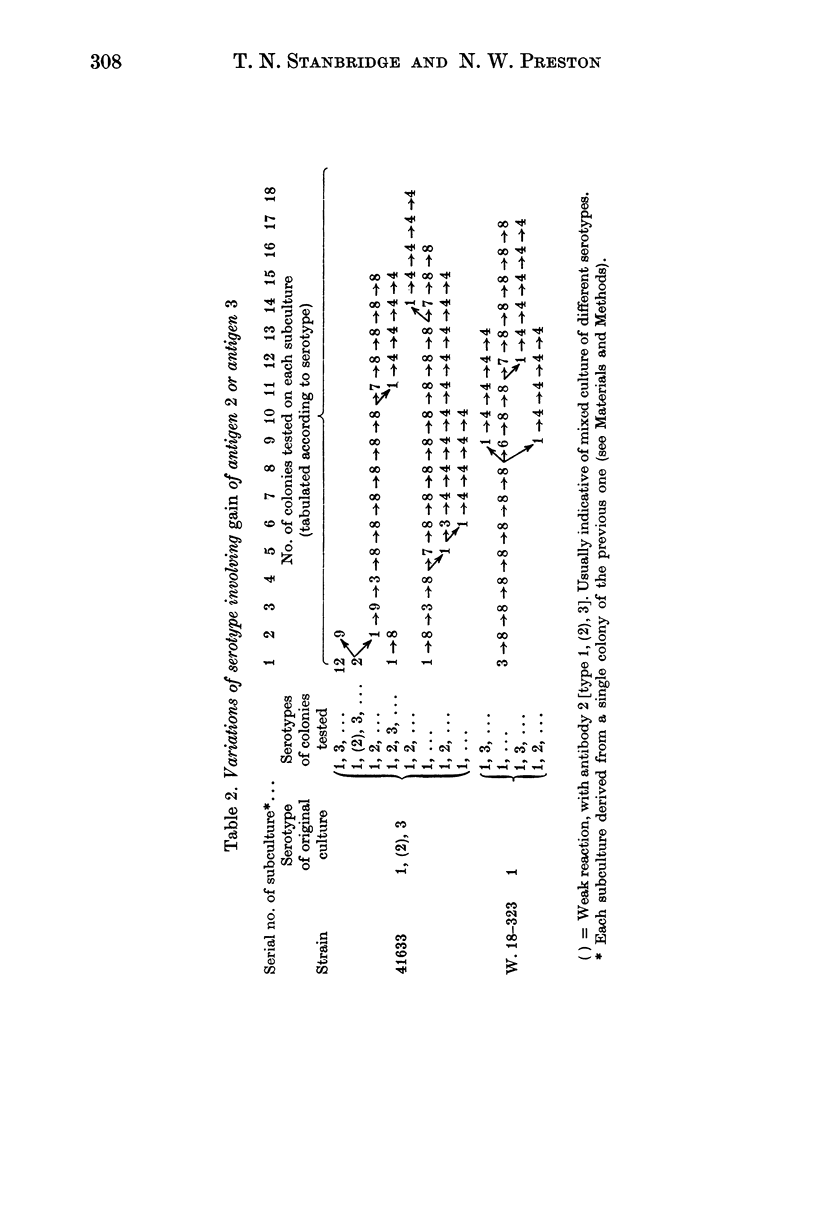
The four main serotypes of Bordetella pertussis (1, 2, 3; 1, 2; 1, 3; 1) undergo spontaneous variation involving loss or gain of antigen 2 or antigen 3. By serial subculture from single colonies on charcoal-blood-agar medium, we have detected loss-mutations from type 1, 2, 3 to 1, 2 or 1, 3, and from type 1, 2 to type 1. Likewise we have found gain-mutations from type 1 to 1, 2 or 1, 3, and from 1, 2 to 1, 2, 3.
These mutations apparently occur with a high frequency in some strains. Other strains have a lower mutation-rate and are more stable antigenically. We have not detected, by this method, either gain- or loss-mutations from the type 1, 3 strains that we have tested.
These findings offer an explanation for the changes in serotype that occur during the course of a pertussis infection in the child and in the marmoset. They also constitute a warning on the possible antigenic instability of laboratory strains, especially relevant in the production, absorption and testing of diagnostic antisera and in the preparation of pertussis vaccine.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN E. K. Serological studies on H. pertussis H. parapertussis and H. bronchisepticus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1953;33(2):202–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1953.tb01512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. Variation in Bordetella pertussis. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(2):367–374. doi: 10.1002/path.1700940216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACEY B. W. Antigenic modulation of Bordetella pertussis. J Hyg (Lond) 1960 Mar;58:57–93. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400038134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston N. W. Potency tests for pertussis vaccines: doubtful value of intracerebral challenge test in mice. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):173–179. doi: 10.1002/path.1700910121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston N. W., Stanbridge T. N. Efficacy of pertussis vaccines: a brighter horizon. Br Med J. 1972 Aug 19;3(5824):448–451. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5824.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston N. W. Technical problems in the laboratory diagnosis and prevention of whooping-cough. Lab Pract. 1970 May;19(5):482–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge T. N., Preston N. W. Experimental pertussis infection in the marmoset: type specificity of active immunity. J Hyg (Lond) 1974 Apr;72(2):213–228. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400023421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


