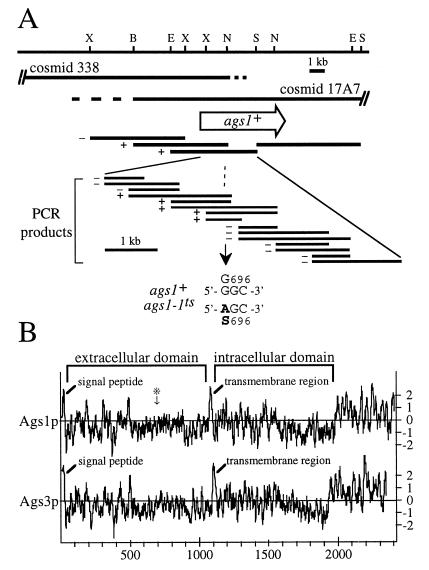
Figure 5.
Characterization of the ags1+ locus and gene product. (A) Restriction map of the ags1+ gene locus and mutation site of the ags1–1ts allele. Both cosmid c17A7 and 338 rescue the ts and cell shape phenotypes of ags1–1 cells. The extent of overlap of the two cosmids has not been mapped precisely (indicated by dashed lines). The open arrow indicates the location and orientation of the ags1+ ORF. The ability of genomic fragments and PCR amplification products to rescue the ts phenotype is indicated to the left of each fragment by + or −. DNA sequence analyses of PCR amplification products identified the ags1–1ts mutation site as codon 696, which was changed from a Gly to a Ser codon. B, BamHI; E, EcoRI; N, NheI; S, SalI; X, XhoI.(B) Predicted topologies of the ags1+ and ags3+ gene products. Hydropathy plots (20) were generated by using a window size of 13. ∗ indicates the ags1–1ts mutation site. Like Ags1p, the Ags3 protein contains an amino-terminal signal peptide predicted to be cleavable (between residues 22 and 23), a single membrane-spanning region at residues 1091–1107, and a multipass transmembrane domain. Only partial sequence is known for Ags2p.