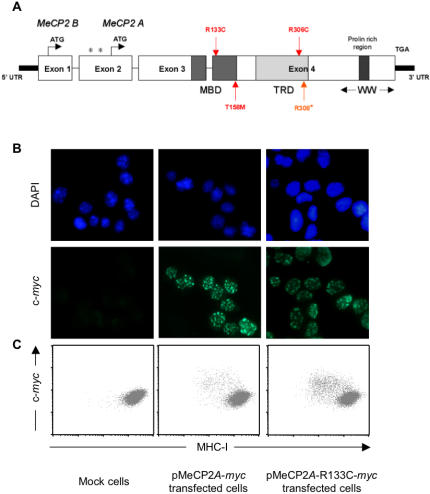
Figure 3. Mutant forms of MeCP2 that cause RTT retain their repressive effect on MHC class I expression.
Panel A: Schematic representation of the MeCP2 protein. Red and orange arrows indicate the positions of the mutations introduced in MeCP2 by site-directed mutagenesis (MBD: methyl-CpG binding domain, TRD: transcription repression domain, WW: group II WW-domain-binding region). Panel B: N2A cells transfected with empty pcDNA3.1 (mock cells), with pcDNA3.1 expressing Myc-tagged MeCP2A (pMeCP2A-myc) or with pcDNA3.1 expressing Myc-tagged MeCP2A with the R133C point mutation (pMeCP2A-R133C-myc) were stained with mouse anti-Myc 9E10 monoclonal antibody, and FITC-labelled anti-mouse IgG antibody. Coverslips were mounted in DAPI-containing ProLong Gold antifade reagent (Molecular Probes) before observation by fluorescence microscopy. Panel C: N2A cells transfected as in panel B were double immunostained for cell surface MHC class I and intracellular Myc-tagged MeCP2, then analysed by flow cytometry. Similar data were obtained for all four mutated forms of MeCP2A and MeCP2B (not shown), and these observations were reproduced in three independent transfection experiments.