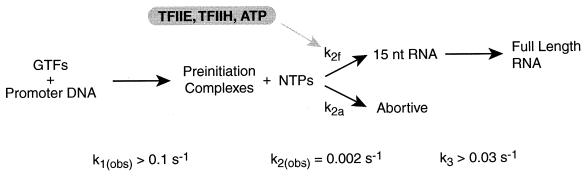
Figure 6.
A model to describe the mechanism of single-round transcription. The rate constant for preinitiation complex formation, k1(obs), is greater than 0.1 s−1, and the rate constant for transcript elongation, k3, is greater than 0.03 s−1 under our standard in vitro transcription conditions. Promoter escape limits the rate of transcription with an observed rate constant, k2(obs), of 2 × 10−3 s−1. In the model, there are two pathways for promoter escape, functional and abortive, with rate constants k2f and k2a, respectively. TFIIE and TFIIH, in an ATP-dependent reaction, increase k2f and, in doing so, increase the fraction of preinitiation complexes that functionally escape the promoter. This is observed experimentally as an increase in the extent of transcription with no significant change in k2(obs) (explained in detail in Discussion).