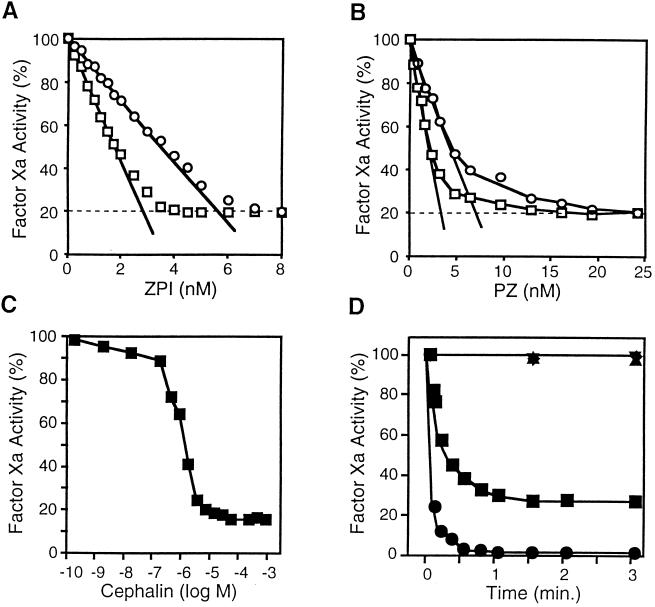
Figure 3.
PZ-dependent inhibition of factor Xa by ZPI. (A) ZPI dose/response. Reaction mixtures containing factor Xa (2.5 or 5.0 nM), CaCl2 (4 mM), cephalin (15 μM), and PZ (40 nM) were incubated with increasing concentrations of ZPI for 15 min at 22°C before remaining factor Xa activity was determined by amidolytic assay. The molar concentration of ZPI was estimated assuming 1.0 mg/ml ZPI produces an A280 of 1.0. (□), Factor Xa, 2.5 nM; (○), factor Xa, 5.0 nM. (B) PZ dose/response. Reaction mixtures containing factor Xa (2.5 or 5.0 nM), CaCl2 (4 mM), cephalin (15 μM), and ZPI (10 nM) were incubated with increasing concentrations of PZ for 15 min at 22°C before remaining factor Xa activity was determined by amidolytic assay. (□), Factor Xa, 2.5 nM; (○), factor Xa, 5.0 nM. (C) Cephalin dose/response. Reaction mixtures containing factor Xa (2.5 nM), CaCl2 (4 mM), PZ (40 nM), and ZPI (10 nM) were incubated with increasing concentrations of cephalin for 15 min at 22°C before remaining factor Xa activity was determined by amidolytic assay. (D) Time course of factor Xa inhibition by PZ/ZPI. Reaction mixtures containing factor Xa (5.0 nM), with or without CaCl2 (4 mM), with or without cephalin (15 μM), and with or without PZ (40 nM) were incubated 5 min at 22°C before the addition of ZPI (10 nM). At the specified times thereafter remaining factor Xa activity was determined by coagulation assay or amidolytic assay. Coagulation assay: (•), with all reactants. Amidolytic assay: (■), with all reactants; (▾), without CaCl2; (▴), without cephalin; (⧫), without PZ.