Figure 9.
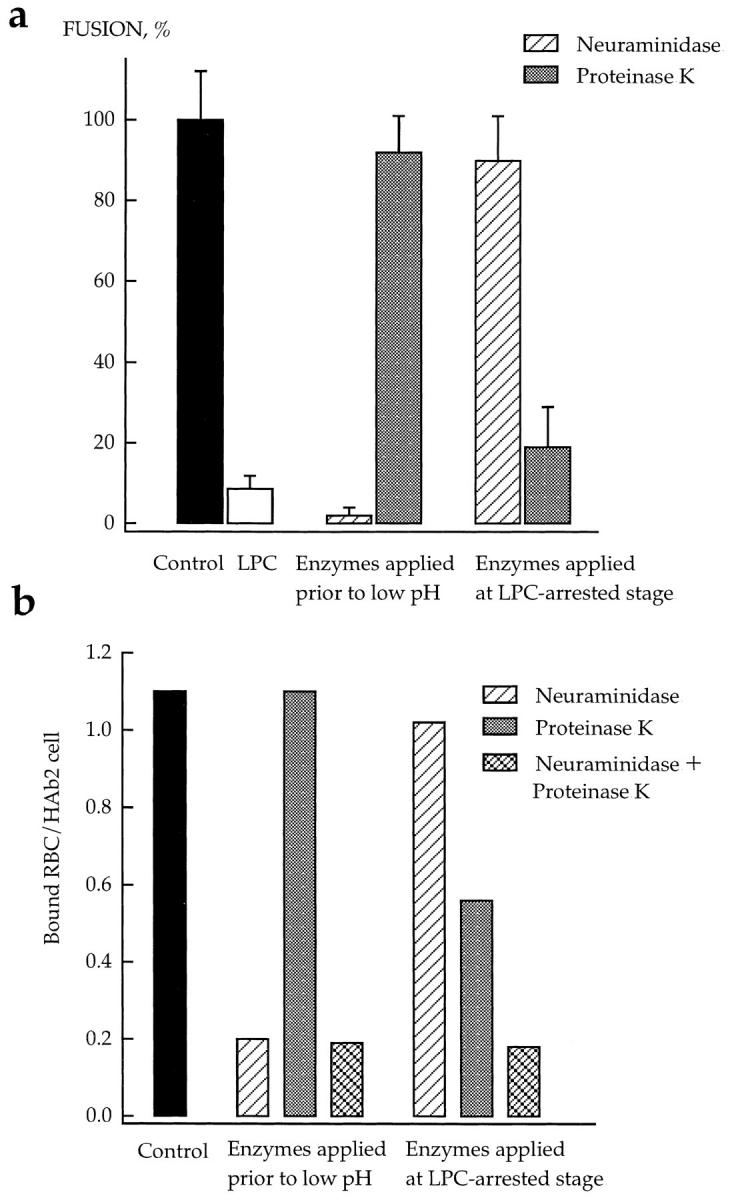
Effects of neuraminidase and proteinase K on the LPCarrested stage of HA-mediated fusion. Fusion of HAb2 cells with prebound R18-labeled RBCs was triggered by a 3-min pH 4.9 pulse applied in the presence of 50 μM lauroyl LPC. After a 20min incubation of cells at neutral pH in LPC-containing PBS, lysolipid was removed by washing cells with LPC-free PBS. Cells were treated by neuraminidase or proteinase K before low pH application or at the LPC-arrested fusion stage in the time interval between the end of low pH and removal of LPC. (a) Fusion. The extent of fusion after removal of LPC was measured as R18 redistribution using fluorescence microscopy, and normalized to those in the control experiments (▪, neither LPC nor enzymes applied). □, the extent of fusion observed at t = 2 hours in the experiments when LPC was not removed. ▨ and ▒⃞ , cells were treated with neuraminidase or proteinase K, respectively. Each point is mean ± SEM, n = 3. (b) Binding. In this representative experiment, the effects of neuraminidase (▨ ) or proteinase K (▒⃞ ), or the combination of both enzymes (▩ ) on binding of R18labeled RBCs to HAb2 cells before low pH application and during the LPC-arrested fusion stage were evaluated with fluorescence microscopy by counting RBCs bound to ∼100 HAb2 cells. ▪, An average number of RBCs bound per one HAb2 cell in the control experiments with neither LPC nor enzymes applied.
