Figure 9.
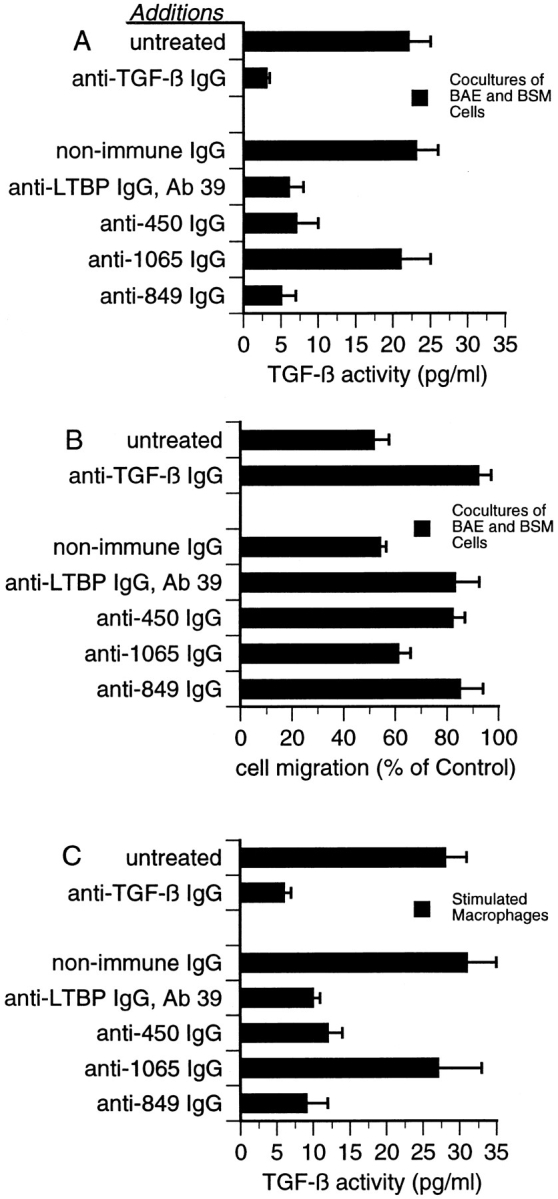
Effect of antibodies to LTBP-1 on latent TGF-β activation by cocultures of BAE and BSM cells, and stimulated macrophages. (A) The MLEC-luciferase assay was used to detect TGF-β activity generated by cocultures of BAE and BSM cells. Serum-free CM harvested from either untreated cultures or cultures treated with 10 μg/ml Ab 39 IgG, 50 μg/ml nonimmune IgG, or 50 μg/ml of affinity-purified anti-450, anti-1065, or anti849 IgG were assayed using the MLEC-luciferase assay. To verify that luciferase production was TGF-β–dependent, 20 μg/ml neutralizing anti–TGF-β IgG was added to CM from untreated cultures. Data presented are from one out of four experiments yielding similar results. (B) The wound migration assay was used to detect TGF-β activity generated by cocultures of BAE and BSM cells. Serum-free CM harvested from untreated cocultures or cocultures treated with the same antibodies as in A were assayed for TGF-β activity using the wound migration assay described in Materials and Methods. Control (100%) is the migration observed in wounded BAE cultures treated with media from homotypic BAE and BSM cells mixed 4:1. These data are presented as the percentage of migration observed in wounded cultures treated with control media. Data are representative of four experiments yielding similar results. (C) The MLEC-luciferase assay was used to detect TGF-β activity generated by stimulated macrophages. Serum-free CM from either untreated or antibodytreated cultures of LPS-stimulated thioglycollate-elicited peritoneal macrophages were harvested and assayed. Antibody treatments were as in A and B. Data presented are from one out of three experiments yielding similar results.
