Figure 2.
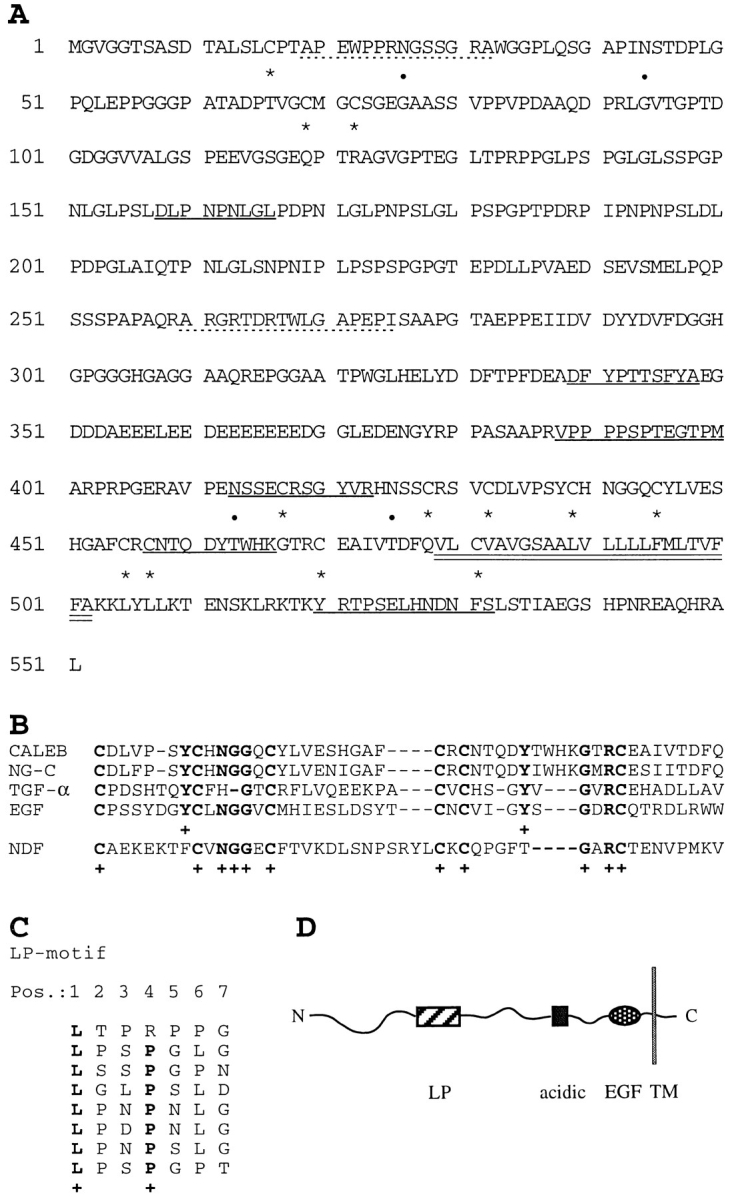
Amino acid sequence, schematic representation of CALEB, and alignments. (A) The amino acid sequence of CALEB deduced from six overlapping cDNA clones is shown using the single letter code. Numbering of amino acids is given at the left. The open reading frame contains 551 amino acids. Dotted lines correspond to the NH2-terminal sequences of the 200-, 140-, and 80-kD components of CALEB obtained by Edman degradation. Sequences obtained from peptides of digests of trypsin or Asp-N of CALEB are underlined and cysteine residues and potential N-glycosylation sites are marked by asterisks and dots, respectively. The putative transmembrane domain is indicated by double underlining. The NH2-terminal peptide sequences of the 200-, 140-, and the 80-kD component are APEWPPRXGXSGRA (aa 19–32) and ARGRXDRTWLGAPEPI (aa 260–275), respectively (X denotes an amino acid not to be defined by peptide sequencing). Sequences from proteolytic digests are DLPNPNLGL (aa 158–166), DFYPTTSFYA (aa 339–348), VPPPPSPXEGTPM (aa 388–400), XSSEXRSGYVR (aa 413–423), XNTQDYTXXK (aa 457–466), and XRTPSEXHNDNFX (aa 520–532). The nucleotide sequence data are available from EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ under accession number Y09264. (B) Alignment of the amino acid sequences of the EGF-like domains and flanking COOHterminal residues of CALEB (chick) with neuroglycan-C (NG-C, rat; Watanabe et al., 1995), transforming growth factor α (TGF-α, rat; Marquardt et al., 1984), epidermal growth factor (EGF, mouse; Gray et al., 1983), or neuregulin-α (NDF, rat; Wen et al., 1992). Alignments obtained by the programs bestfit and clustal of the HUSAR program package and by visual inspection start at the most NH2-terminal cysteine residue of the EGF motifs. Dashes indicate gaps that were introduced for maximal alignment. Identical residues corresponding to amino acids of CALEB are printed in bold and marked by a cross. (C) The amino acid sequence of CALEB at residues 131 to 186 comprises a stretch of primarily uncharged amino acids enriched in leucines and prolines, designated LP-motif. A stretch of seven amino acids repeated eight times contains a leucine at position 1 and a proline at position 4 (one exception). The periodicity of the leucine residues within the LP-motif resembles that of a leucine zipper; however, because of the existence of prolines, it is unlikely that this element of CALEB forms an α-helical structure as defined for leucine zippers. (D) Schematic representation of the overall structure of CALEB. LP, the leucine/proline-motif; acidic, the acidic box that is highly enriched in aspartic and glutamic acids; EGF, the EGF-like domain. A transmembrane segment (TM) separates these segments from a short cytoplasmic stretch.
