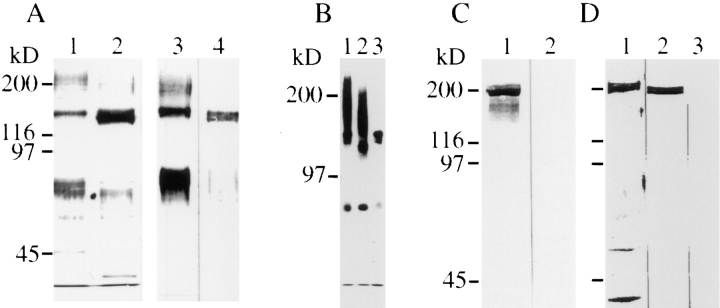
Figure 3.
CALEB components in neural tissues. (A) Polypeptides isolated by immunoaffinity chromatography using mAb 4/1 from embryonic (lane 1) or adult retinas (lane 2) analyzed by 7% SDSPAGE followed by silver staining. Immunotransfer analysis of CALEB isolates from embryonic (lane 3) or adult retinas (lane 4) using mAb 4/1. (B) CALEB components after biosynthetical labeling with [35S]sulfate of retinal monolayer cultures in vitro (lane 1) followed by digestion with neuraminidase (lane 2) or chondroitinase ABC (lane 3). Bands were visualized by fluorography. (C) TN-C copurifies with CALEB from embryonic retinas. CALEB was isolated from embryonic retinas by immunoaffinity chromatography by omitting the high-salt washing step, subjected to SDSPAGE (7%), and analyzed in immunotransfers using mAb 68 directed to TN-C (lane 1) or mAb 23-13 to TN-R (lane 2). (D) The highsalt fraction of anti-CALEB columns consists of TN-C. The CALEB immunoaffinity column loaded with detergent extracts of embryonic retinas followed by washing with solubilization buffer was preeluted with three column volumes of 1.2 M NaCl in PBS. The highsalt fraction was analyzed in SDS-PAGE followed by silver staining (lane 1) or analyzed in immunotransfers using mAb 68 to TN-C (lane 2) or mAb 23-13 to TN-R (lane 3). Molecular mass markers are indicated at the left of each panel.