Figure 1.

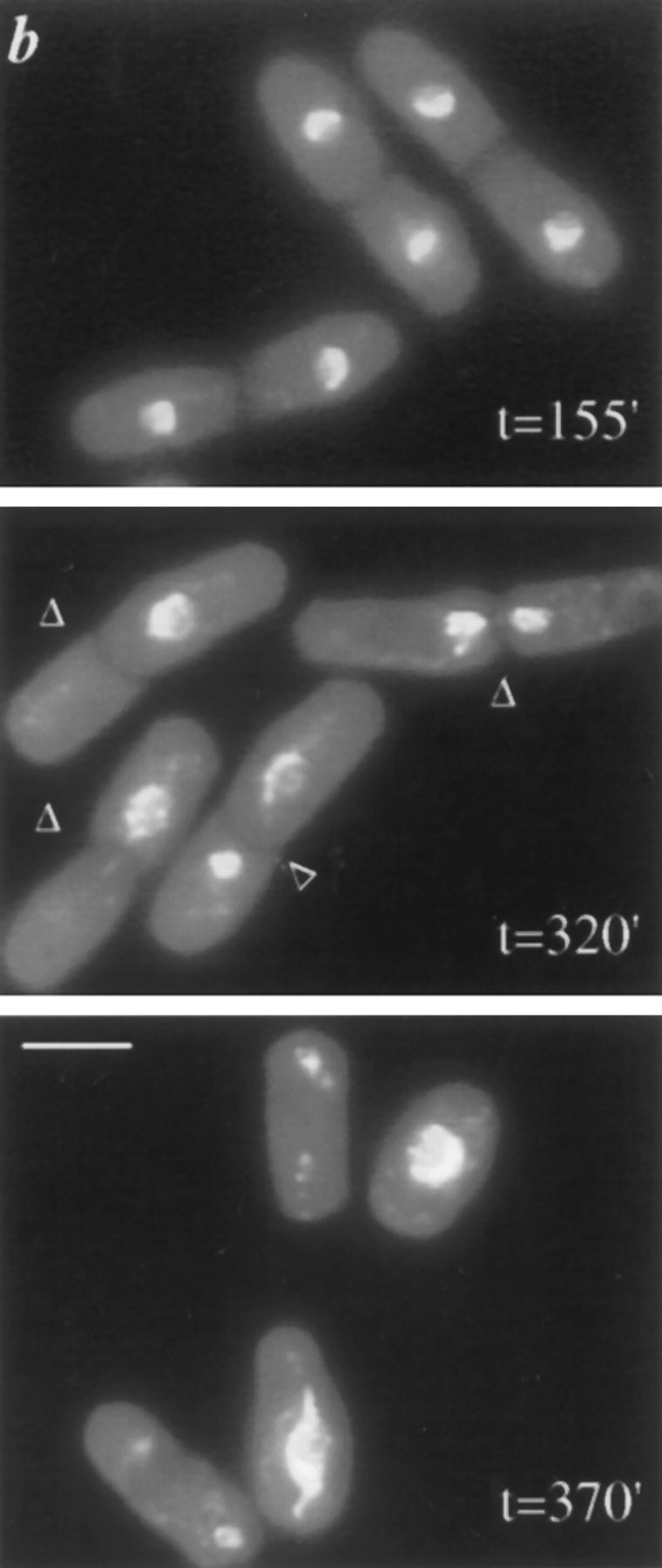
A synchronized population of dim1-35 mutant cells shifted to restrictive temperature displays a second cell cycle arrest. dim1-35 mutant (KGY392) or wildtype (KGY28) cells were grown to midlog phase in rich medium at permissive temperature (25°C). Cells were synchronized in early G2 by centrifugal elutriation and then inoculated into rich medium at 36.5°C. Samples were collected at 20- to 25min intervals and subjected to various analyses. (a) DNA content of dim1-35 mutant cells after shift to restrictive temperature. Cells were fixed with ethanol, stained with propidium iodide, and subjected to flow cytometric analysis. DNA content, expressed in arbitrary units, is shown on the horizontal axis. Cell number is shown on the vertical axis. (b) Cell and nuclear morphology of dim1-35 cells at the first peak of septation (top), at the second peak of septation (middle), and after the second round of septation (bottom). Cells were fixed with ethanol and stained with DAPI. Arrowheads indicate septa. (c) Septation index of dim1-35 (○) or wild type (•) cells after shift. (d) Percent viability (○), percentage of cells containing 2C DNA (▵), and septation index (□) of dim1-35 mutant cells after shift. Note that viability begins to decline sharply at t = 230 min, just before septated cells are first observed at t = 250 min. (e) Tubulin and SPB staining of dim1-35 mutant cells at second peak of septation after shift to restrictive temperature. (Left) DNA stained with DAPI. (Middle) Tubulin stained with TAT1 antibody. (Right) SPBs stained with α-Sad1p antibody. Note that septation has occurred, bisecting the elongated spindle and producing two daughter cells, one containing the undivided nucleus (*) and one containing no chromatin (**). Arrowheads indicate septa; arrows indicate SPBs. Bars: (b) 5 μm; (e) 3 μm.


