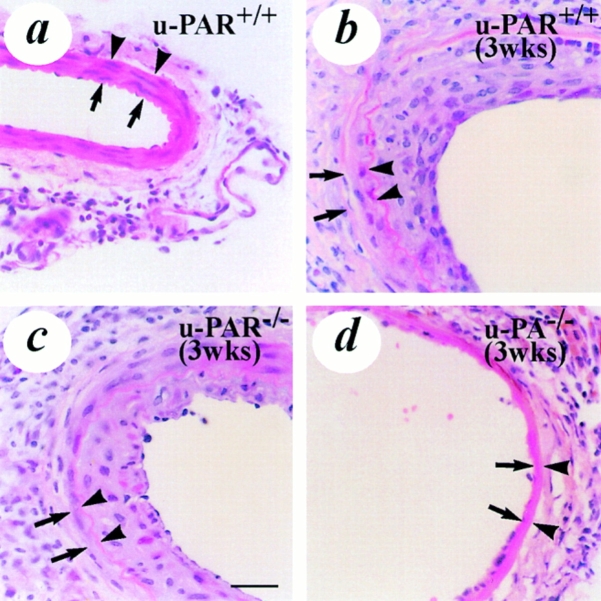
Figure 2.
Light microscopic analysis of vascular wound healing and neointima formation after electric injury. All sections were stained with hematoxylin-eosin. (a) uninjured u-PAR+/+ artery, revealing the presence of smooth muscle cells in the media. (b–d) artery from a u-PAR+/+ (b) and a u-PAR−/− (c) mouse (at location 5 as defined in Fig. 1) 3 wk after injury, revealing a similar neointima in u-PAR−/− as in u-PAR+/+ arteries. For comparison, an electrically injured artery from a u-PA−/− mouse (d), revealing impaired wound healing and a much smaller neointima is displayed (reproduced from reference 9). The arrows indicate the internal elastic lamina whereas the arrowheads indicate the external elastic lamina. Bar, 50 μm.