Figure 10.
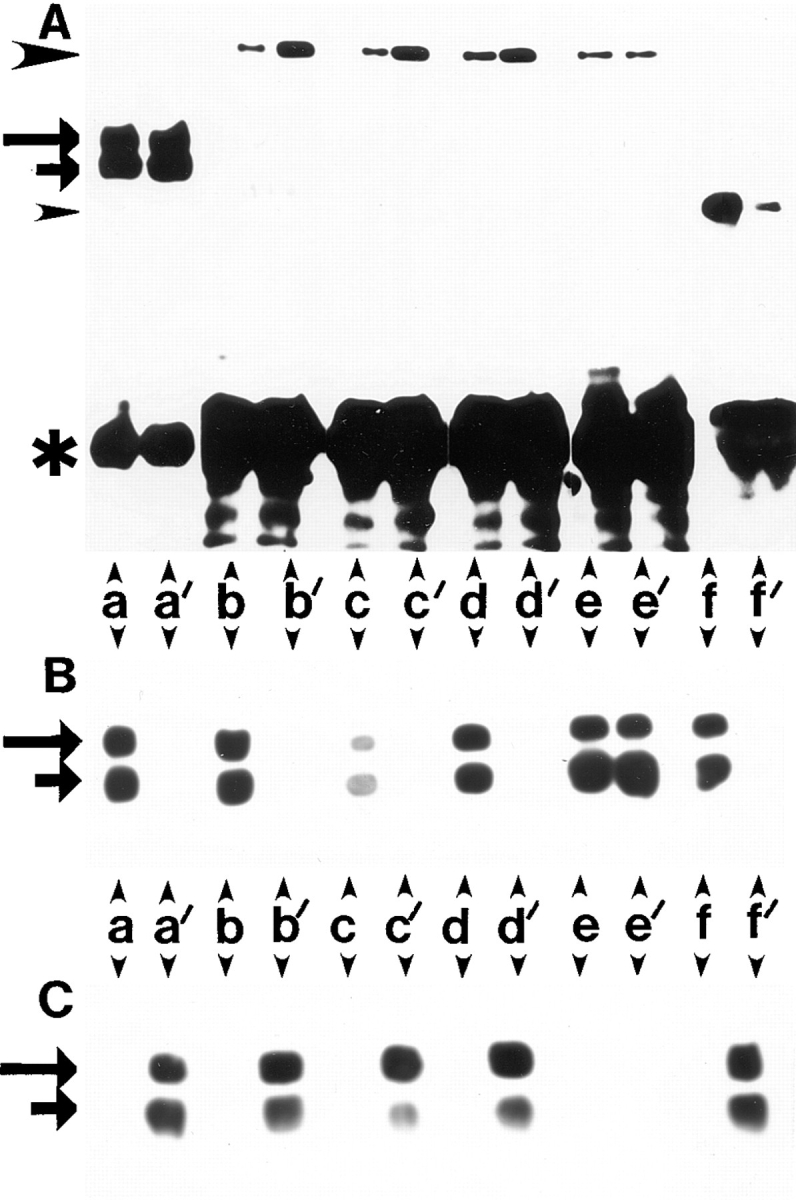
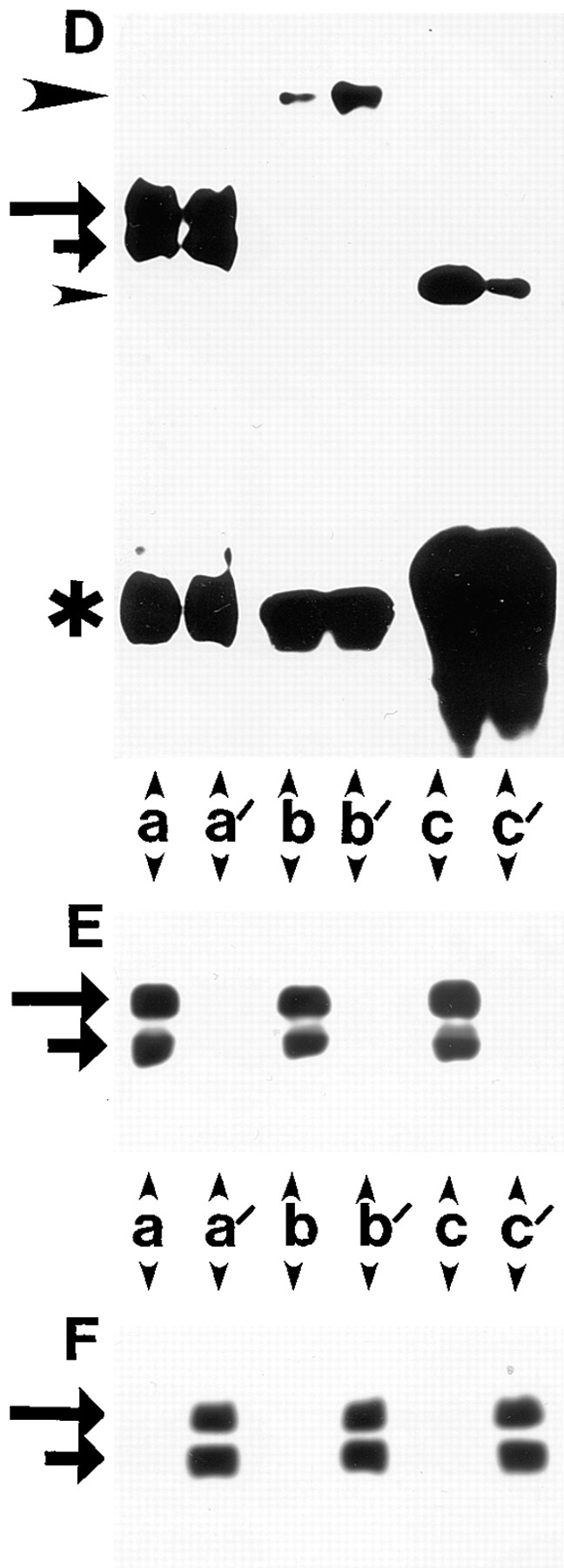
Differential association of β1A and β1D integrins with talin and α-actinin. (A and D) Coimmunoprecipitation of talin and α-actinin with β1D and β1A integrins. (A) CHO transfectants. Human β1A (a–d, and f) or β1D (a′–d′, and f′ ) integrins were immunoprecipitated with TS2/16 mAb (a, a′, b, b′, f, and f ′) or activation-dependent 12G10 mAb either in the absence of Mn2+ (c and c′) or in the presence of 1 mM Mn2+ (d and d′ ). Endogenous hamster β1A was immunoprecipitated from β1A-CHO (e) or β1D-CHO (e′ ) cells with 7E2 mAb. Immunoprecipitates were probed for β1 integrin (a and a′ ), talin (b, b′, c, c′, d, d′, e, and e′ ), or α-actinin (f and f ′ ). (D) GD25 transfectants. Human β1A (a–c) or β1D (a′–c′ ) integrins were immunoprecipitated with TS2/16 mAb and immunoprecipitates were probed for β1 integrin (a and a′ ), talin (b and b′ ), or α-actinin (c and c′ ). Long and short arrows mark the β1 integrin doublet (mature form and precursor, respectively). Large arrowheads point to talin and small arrowheads mark α-actinin. Asterisks indicate IgG heavy chains. (B, C, E, and F) The same immunoprecipitates as in A were probed for β1A (B) or β1D (C) integrins with the isoform-specific antibodies. The same immunoprecipitates as in D were blotted for β1A (E) or β1D (F).
