Figure 1.
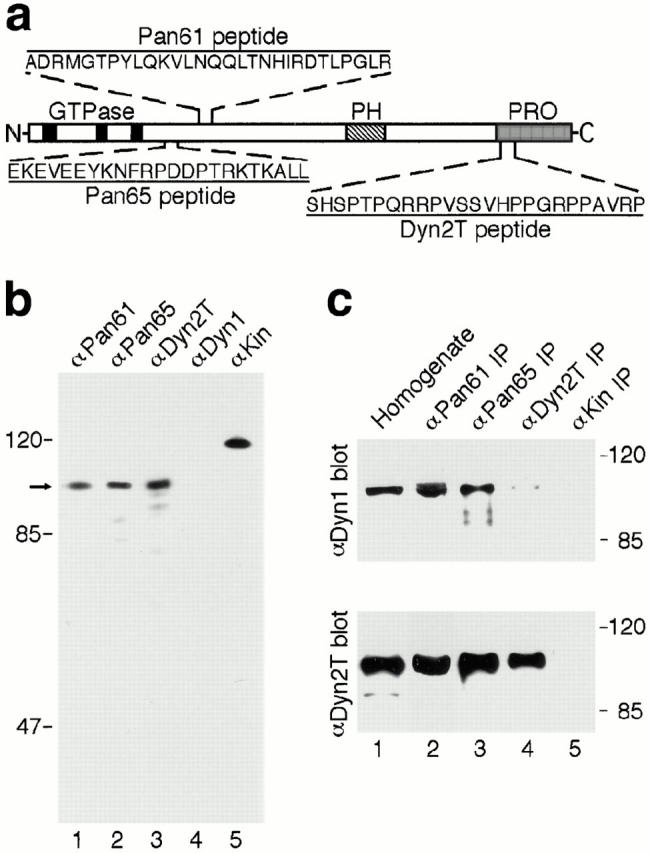
Characterization of dynamin-specific antibodies. (a) Diagram depicting the portions of dynamin to which anti-peptide antibodies were made. Two regions (Pan61 and Pan65) are located within the NH2-terminal “head” domain near the last of three GTP-binding elements (black boxes) and are conserved among the different dynamin isoforms. A third region (Dyn2T) is located within the proline-rich COOH-terminal “tail” domain (PRO, shaded region) and is unique to Dyn2. The location of the pleckstrin homology domain is indicated (PH, striped box). (b) Antibodies to the Pan61, Pan65, and Dyn2T peptides react with dynamin specifically by Western blot analysis. A cytosolic fraction was prepared from rat liver and then subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis using the anti-Pan61 (lane 1), anti-Pan65 (lane 2), and anti-Dyn2T (lane 3) antibodies, or polyclonal antibodies that are specific for Dyn1 (lane 4) and kinesin (lane 5) as controls. A prominent dynamin band at ∼100 kD (arrow) was detected with the anti-Pan61, anti-Pan65, and anti-Dyn2T antibodies but not with the anti-Dyn1 antibody, since Dyn1 is not expressed in epithelial tissues. The anti-kinesin antibody recognized a characteristic ∼120-kD band. The positions of molecular mass standards are on the left. (c) The anti-Pan61 and anti-Pan65 antibodies immunoprecipitate both Dyn1 and Dyn2 from rat brain, whereas the anti-Dyn2T antibody is specific for Dyn2. Dynamin was immunoprecipitated from a crude brain homogenate (lane 1) using affinity-purified anti-Pan61 (lane 2), anti-Pan65 (lane 3), and anti-Dyn2T (lane 4) antibodies. Control immunoprecipitates were obtained with the anti-kinesin antibody (lane 5). The starting brain homogenate and subsequent immune complexes were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis with either a Dyn1-specific antibody (top) or the anti-Dyn2T antibody (bottom). Both Dyn1 and Dyn2 precipitated with the anti-Pan61 and anti-Pan65 antibodies, whereas the anti-Dyn2T antibody precipitated Dyn2 specifically, with only trace amounts of Dyn1 detected.
