Figure 1.
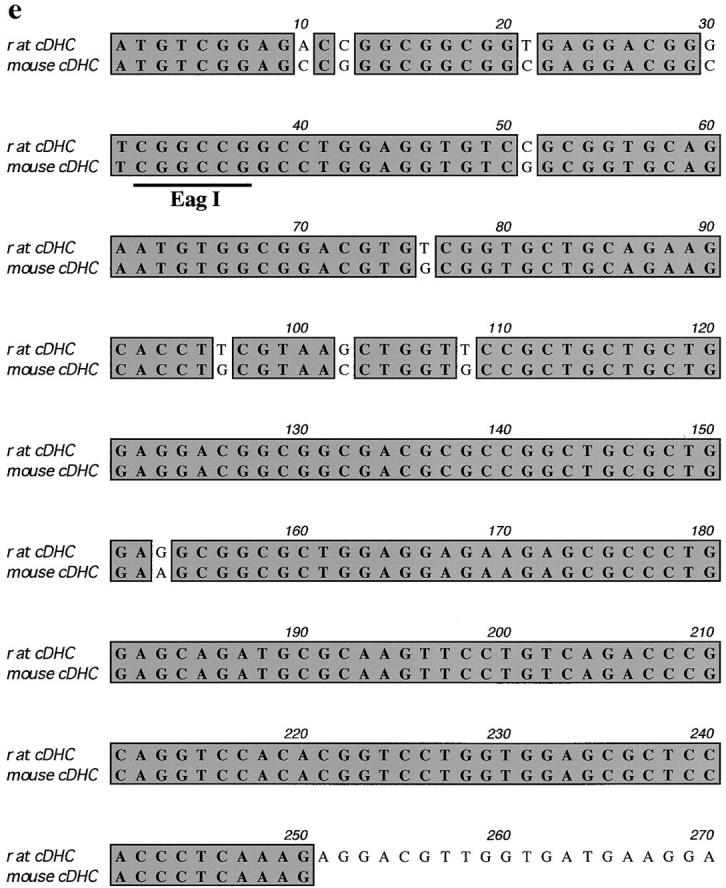
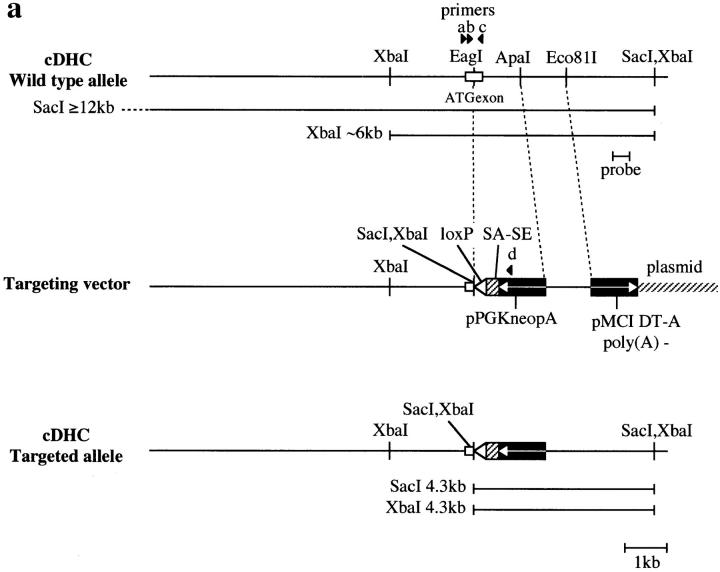
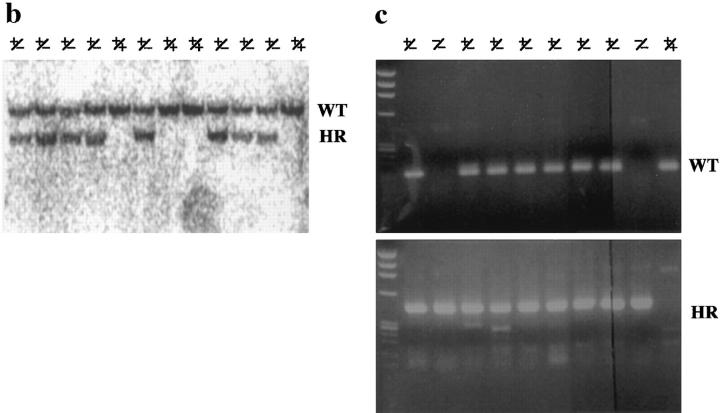
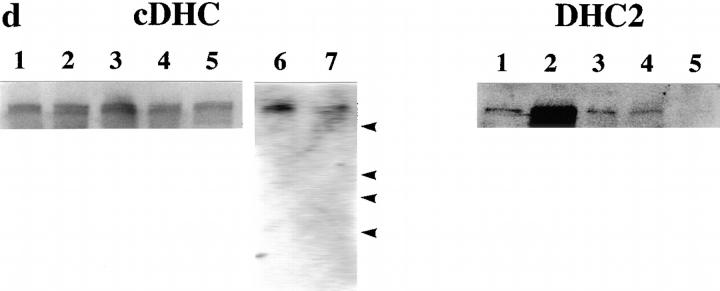
Targeted inactivation of the cDHC gene in ES cells and mice. (a) The cDHC gene locus and targeting vector. (Top) cDHC wild-type allele. (Middle) Replacement-type targeting vector. (Bottom) Targeted allele after homologous recombination. (b) Southern blot analysis of representative genomic DNA of 12.5-dpc embryos from cDHC heterozygote intercrosses. Embryonic DNA was digested with SacI, and Southern blot analysis was performed using the 3′-flanking probe. WT, wild-type band; HR, homologous recombinant band. Genotypes: +/+, wild-type;+/−, heterozygote; −/−, homozygote. (c) PCR analysis of genomic DNA of 3.5-dpc embryos from a cDHC heterozygote intercross. DNA samples were subjected to PCR using the primer pairs b/c (wild-type allele) or b/d (mutated allele). (d) Immunoblotting of cDHC (left) and DHC2 (right). (Left) Crude cell extracts from: lane 1, NRK; lane 2, Cos; lane 3, wild-type ES; lane 4, heterozygous mutant ES; lane 5, wild-type ES (half amount); lane 6, wild-type ES; lane 7, heterozygous mutant ES cells were loaded on the gel and blotted with anti-cDHC sera. Arrowheads represent the positions of molecular mass markers (200, 116, 97, and 66 kD, from top to bottom, respectively). (Right) Crude cell extracts from: lane 1, NRK; lane 2, Cos; lane 3, wild-type ES; lane 4, heterozygous mutant ES; lane 5, wild-type ES (half amount) cells. Crude extracts were loaded and blotted with anti-DHC2 sera. (e) The sequence of the open reading frame of the mouse cDHC first coding exon and the cDNA sequence from rat cDHC. The EagI site used for constructing the targeting vector was underlined.