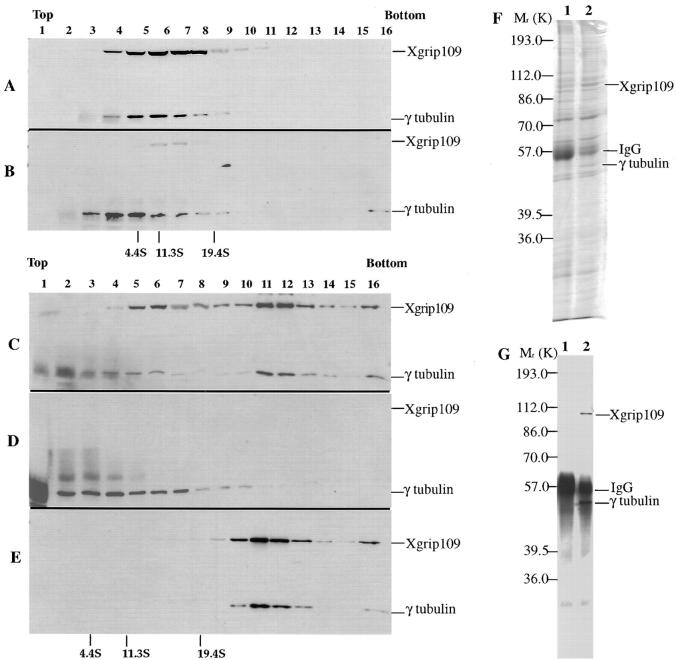
Figure 6.
Xgrip109 is required for the reformation of salt-disrupted γTuRC. Clarified Xenopus egg extracts were precipitated with 30% ammonium sulfate. The pellet fraction (30% Asp) was resuspended in either Hepes 100 as control or in Hepes 1 M. Sucrose gradients in A–E are all 5–40%. (A) 30% Asp resuspended in Hepes 1M was immunoprecipitated with random IgG and then analyzed on a sucrose gradient. (B) The same as in A, except that the anti-Xgrip109 antibody, 109-2, was used in the immunoprecipitation. (C) The same as in A, except that after immunoprecipitation, a desalting step was included before the sucrose gradient sedimentation. (D) The same as in B, except that after immunoprecipitation, a desalting step was included before the sucrose gradient sedimentation. (E) Control, 30% Asp resuspended in Hepes 100, desalted, and fractionated on a sucrose gradient. (F) SDS-PAGE separation followed by Coomassie blue staining of proteins that were immunoprecipitated with random IgG (lane 1) and 109-2 IgG (lane 2). (G) The same protein samples in F were analyzed by Western probing with XenC and 109-2. Because samples in A and B contained higher amounts of salt than that of the samples in C, D, and E (refer to Materials and Methods), the sucrose gradient fractions of A and B cannot be compared directly to that of C, D, and E. The molecular weight standards for A and B are indicated at the bottom of A; C, D, and E are indicated at the bottom of E. Standards used are BSA (4.4S), bovine liver catalase (11.3S), and bovine thyroglobulin (19.4S).