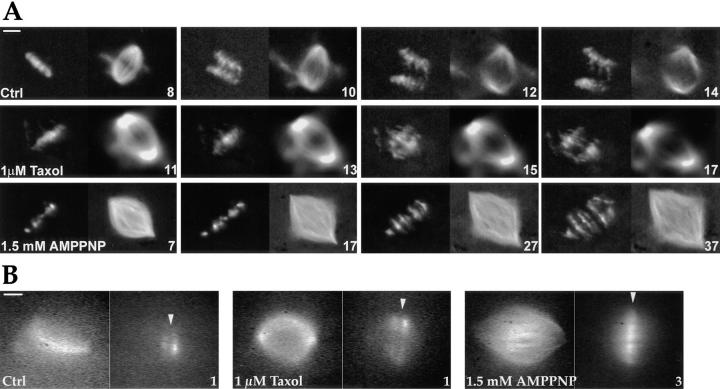
Figure 4.
Pharmacological analysis of anaphase chromosome movement and poleward MT flux in Xenopus extract spindles. (A) Effect of taxol and AMPPNP treatments on chromosome movement and spindle structure during anaphase in vitro. Top row represents a control anaphase (Ctrl), the middle row represents anaphase in 1 μM taxol (1 μM Taxol), and the bottom row represents anaphase in 1.5 mM AMPPNP (1.5 mM AMPPNP). Taxol and AMPPNP were added along with the calcium used to initiate anaphase (t = 0 min). Each time point in the sequence is represented by paired DAPI-labeled chromosome (left) and X-rhodamine tubulin (right) images and the time after calcium addition is stamped in minutes on the lower right corner of the X-rhodamine tubulin image. Note both the much later times after calcium addition and the fivefold larger intervals (10 min vs. 2 min) between consecutive time points for the 1.5 mM AMPPNP sequence. The observed separation of sister chromatids in 1.5 mM AMPPNP is not due to chromosome-to-pole movement but primarily resulting from spindle elongation (see Fig. 5). (B) Effect of taxol and AMPPNP treatments on poleward MT flux. Paired X-rhodamine tubulin and fluorescein tubulin images are shown 1 min (for control and 1 μM taxol–treated spindles) and 3 min (for 1.5 mM AMPPNP–treated spindles) after the fluorescent mark was made on the spindle MTs. The initial position of the mark on the spindle is indicated by a white arrowhead. The 1 μM taxol spindle was marked 8 min after taxol addition. The 1.5 mM AMPPNP spindle was marked ∼10 min after addition of calcium and AMPPNP. Bar-splitting occurs as a result of poleward flux of MTs emanating from opposite spindle poles (Sawin and Mitchison, 1991). The similar extent of splitting of the initially central fluorescent mark is evident in both the control and taxol-treated spindles. Significant bar-splitting is not evident in the presence of 1.5 mM AMPPNP. Even at much later times (up to 10 min after marking the spindle), there is no significant bar-splitting at this AMPPNP concentration (see also Sawin and Mitchison, 1991). Bars: (A) 20 μM; (B) 10 μm.