Figure 2.
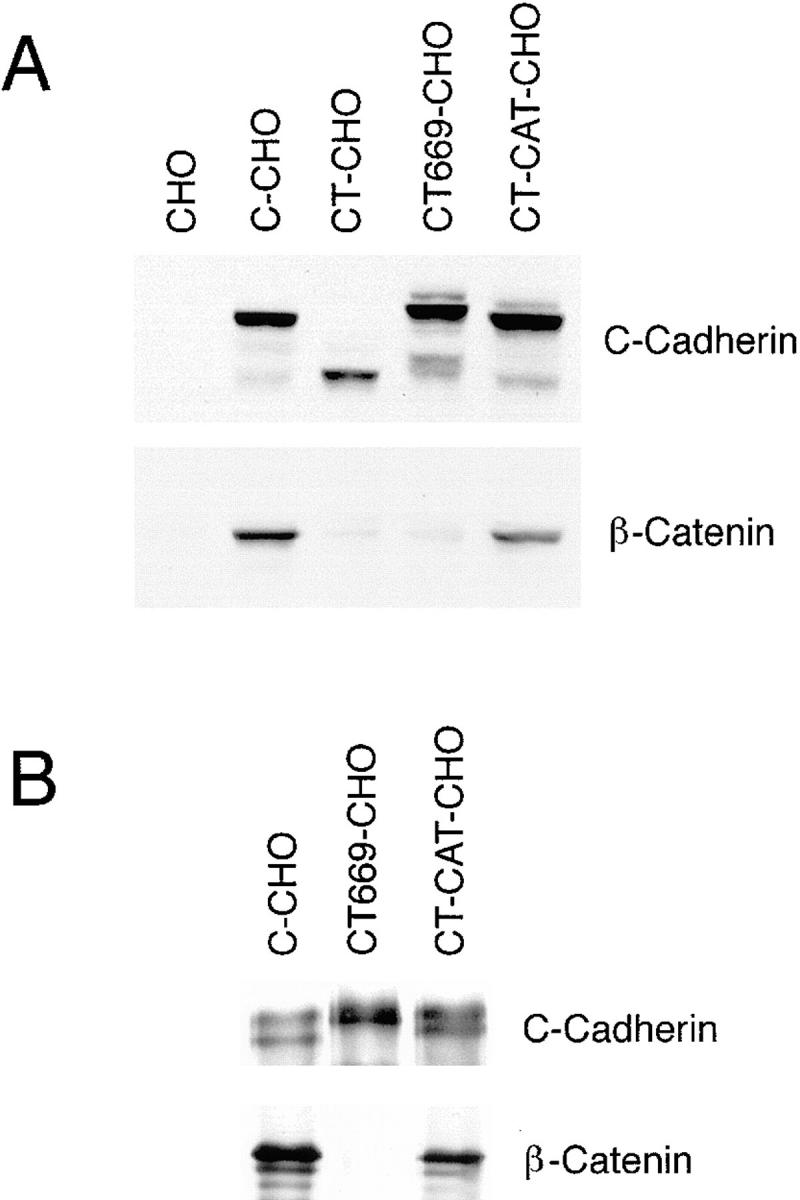
Expression of C-cadherin and mutant cadherin proteins in CHO cells. (A) Comparison between cadherin expression and cellular β-catenin levels. Western blots of lysates from parental CHO cells and CHO cells stably expressing wild-type C-cadherin (C-CHO, clone 12), tailless cadherin mutant (CT-CHO, clone 8), a deletion mutant lacking the catenin-binding region (CT669-CHO, clone A1) and a deletion mutant lacking the juxtamembrane region of the cytoplasmic tail (CT-CAT-CHO, clone 13) were probed for the C-cadherin ectodomain (top), then stripped and reprobed for β-catenin (bottom). Identical amounts of total cellular protein were loaded in each lane. Both the CT669 and CT-CAT mutants display polypeptide bands that run at or slightly higher than wild-type C-cadherin, consistent with the addition of multi-copy myc-epitope tags. Total cellular β-catenin levels were increased in cells expressing wild-type C-cadherin and CT-CAT, but not in cells expressing the CT or CT669 mutants. (B) β-catenin coimmunoprecipitates with wild-type C-cadherin and CT-CAT, but not with CT669. Lysates from C-CHO, CT669-CHO, and CT-CAT-CHO cells were immunoprecipitated with a pAb directed against the C-cadherin ectodomain, transferred to nitrocellulose and probed for C-cadherin (top) or β-catenin (bottom). C-cadherin immunoblots identify mature and precursor forms of the wild-type and mutant cadherins.
