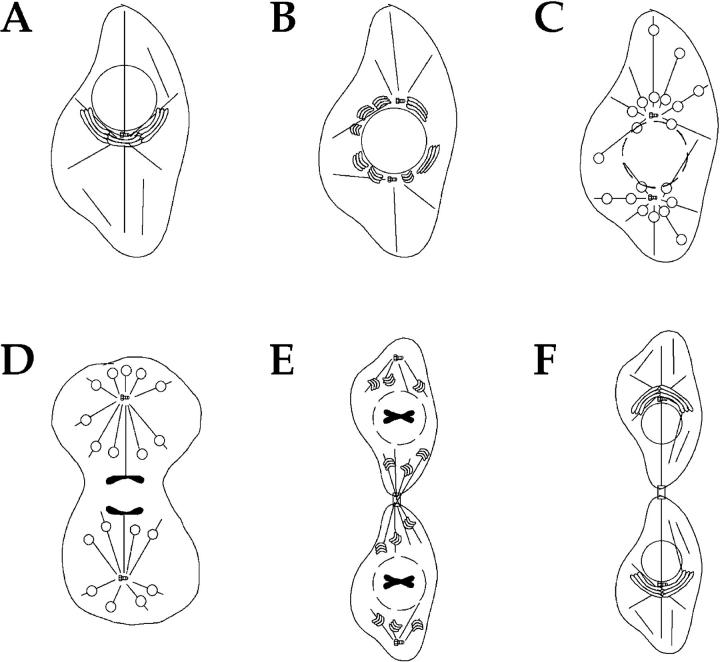
Figure 8.
Model for Golgi apparatus disassembly and partitioning during mitosis. (A) In most cells, the Golgi apparatus exhibits a polarised position in interphase, at one side of the nucleus and next to the centrosome. (B) At the G2/M transition, the Golgi ribbon reorganizes and adopts a more perinuclear localization. This reorganization may be coordinated by the separation of centrosomes, and the association of Golgi membranes with the two microtubules organizing arrays. (C) Fragmentation into Golgi stacks continues throughout prophase, and coincident with nuclear envelope break down, Golgi stacks rapidly fragment to yield mitotic Golgi clusters that are repositioned around the spindle poles and by astral microtubules. (D) As cell division ensues, Golgi clusters associate with microtubules, forming ring-like structures that are partitioned along with each spindle pole and one complement of sister chromatids. (E) At the end of cytokinesis, reformed Golgi stacks are positioned both close to the midbody and to the daughter cell centrosome, then slowly converge to reform the Golgi ribbon as shown in F (Moskalewski and Thyberg, 1990).