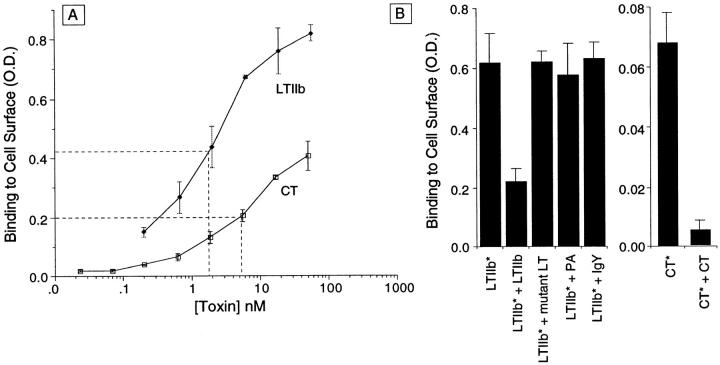
Figure 1.
CT and LTIIb bind specifically with high affinity to intact T84 monolayers. All binding assays were performed in HBSS containing 5% bovine serum albumin. Nonspecific signals in the absence of applied toxins were nearly identical to background (0.09 O.D. units). (A) Binding isotherms for CT and LTIIb applied at 4°C to T84 cells grown on plastic. Polyclonal anti-CT or anti-LTIIb antibodies were used to detect toxin bound at the cell surface. (B) Steady-state binding of biotin-labeled LTIIb (5 nM) or CT (5 nM) to T84 cells at 4°C in the presence of excess unlabeled LTIIb (1 μM), LTG33D B subunit (500 nM), purified anthrax protective antigen (200 nM), chicken IgY (1 μM), or unlabeled CT (1 μM) as indicated. Biotin-labeled toxins are indicated by *. In these studies, enzyme-linked avidin was used to detect toxin bound at the cell surface.