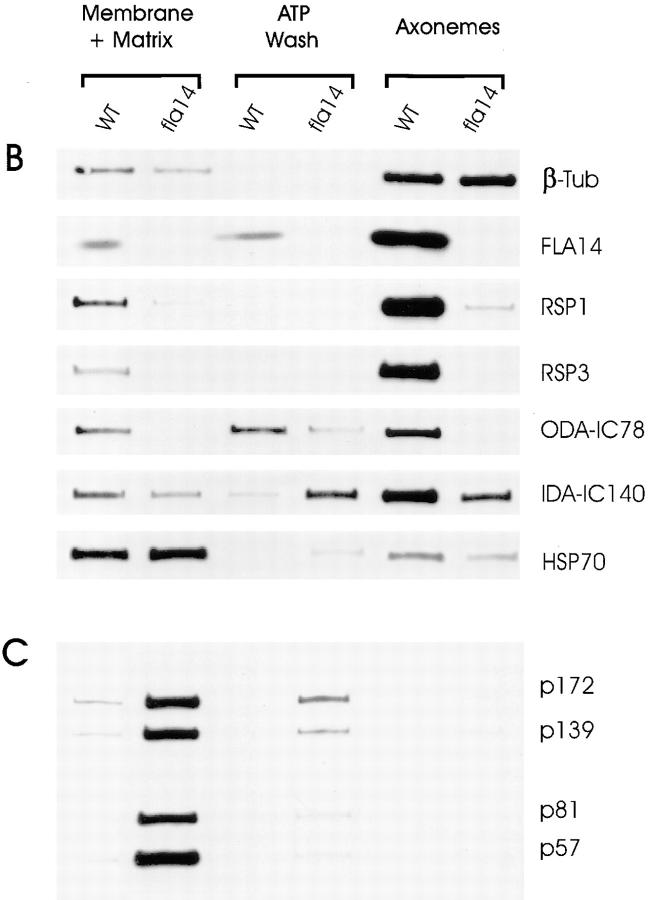
Figure 8.
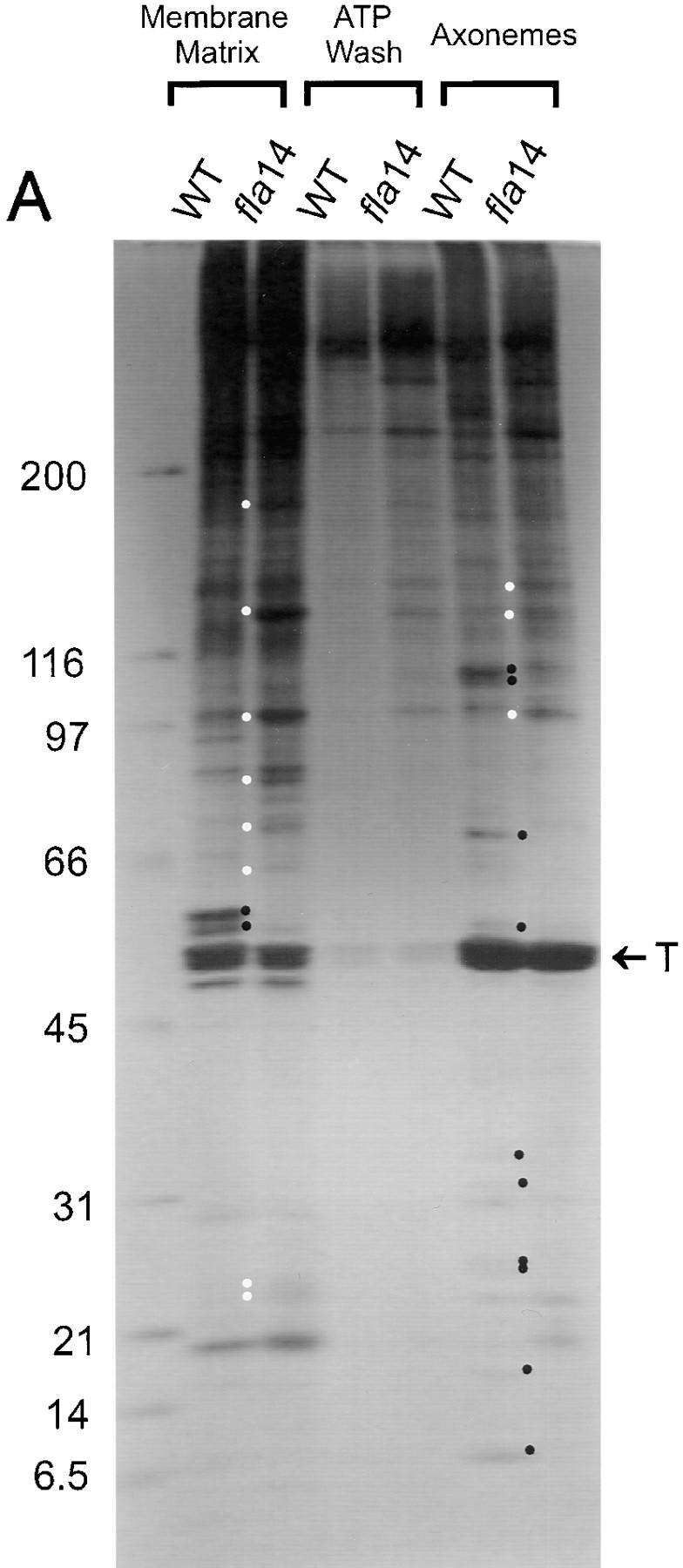
Many flagellar proteins are affected by deletion of the LC8 gene. Flagella were isolated from 137c (WT) and V64 (fla14) cells and separated into the NP-40–soluble fraction (Membrane + Matrix), the fraction of proteins released from the axoneme by 10 mM ATP (ATP Wash), and the remaining axonemal proteins (Axonemes). The proteins within these fractions were separated electrophoretically on SDS 5–15% gradient polyacrylamide gels. Loadings of wild-type and fla14 axonemes were normalized based on β tubulin content (see Fig. 8 B); for each cell type, membrane plus matrix, ATP wash, and axoneme fractions were loaded with protein from an equivalent number of flagella. (A) Silver-stained gel. Proteins that are more abundant or less abundant in fractions of fla14 as compared with wild-type flagella are marked by white or black dots, respectively. In general, the fla14 membrane plus matrix fraction had increased amounts of several proteins, whereas the fla14 axonemes exhibited reduced amounts of several other proteins. (B) Immunoblots probed with antibodies specific for LC8 (FLA14), the outer dynein arm intermediate chain IC78 (ODA-IC78), the I1 inner dynein arm intermediate chain IC140 (IDA-IC140), radial spoke stalk protein RSP1 (RSP1), radial spoke head protein RSP3 (RSP3), the molecular chaperone HSP70 (HSP70), and β tubulin (β-tub). (C) Immunoblot probed with a mixture of monoclonal antibodies against putative raft proteins p172, p139, p81, and p57 (Cole et al., 1998).