Figure 5.
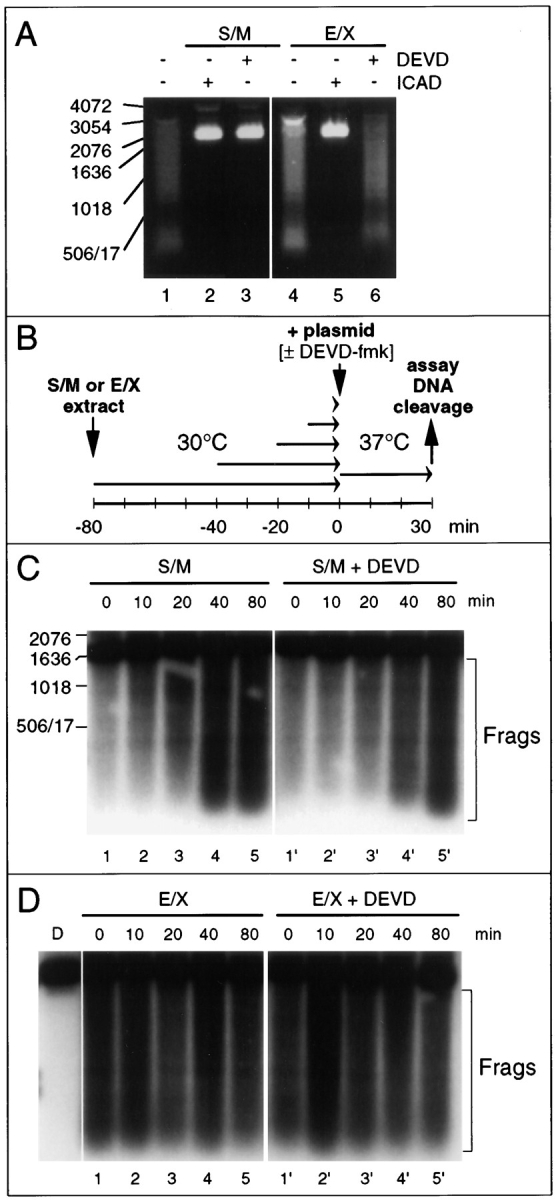
Differences in the activity of the CAD-like nuclease in S/M and E/X extracts. (A) CAD-like nuclease in S/M extracts is sensitive to DEVD-fmk, whereas that in E/X extracts is not. Apoptotic extracts cleave a plasmid substrate at 37°C (lanes 1 and 4). The nuclease responsible is inhibited by purified murine GST-ICAD (lanes 2 and 5) and therefore is functionally related to murine CAD (Enari et al., 1998). In S/M extracts, but not E/X extracts, the nuclease is abolished by addition of DEVD-fmk together with the plasmid DNA (lanes 3 and 6). (B) Diagram of experimental protocol designed to test whether the CAD-like enzyme is active in both S/M and E/X extracts before the incubation with DNA. (C) In S/M extracts, the CAD-like activity increases during preincubation of the extract at 30°C before addition of the plasmid DNA (lanes 1–5). This activity is now insensitive to the addition of DEVD-fmk at the time of plasmid addition (lanes 1′– 5′). Bracket labeled “Frags” indicates the products of caspase cleavage. The DNA cleavage activity in lane 1′ may arise from some limited activation of CAD before all caspases were inhibited since DNA and DEVD-fmk were added at the same time. (D) In contrast, preincubation has no effect on the cleavage of plasmid substrate by E/X extracts (lanes 1–5), which is likewise resistant to inhibition with DEVD-fmk (lanes 1′–5′). Lane D, added plasmid DNA alone. Bracket labeled “Frags” indicates the products of caspase cleavage.
