Figure 1.
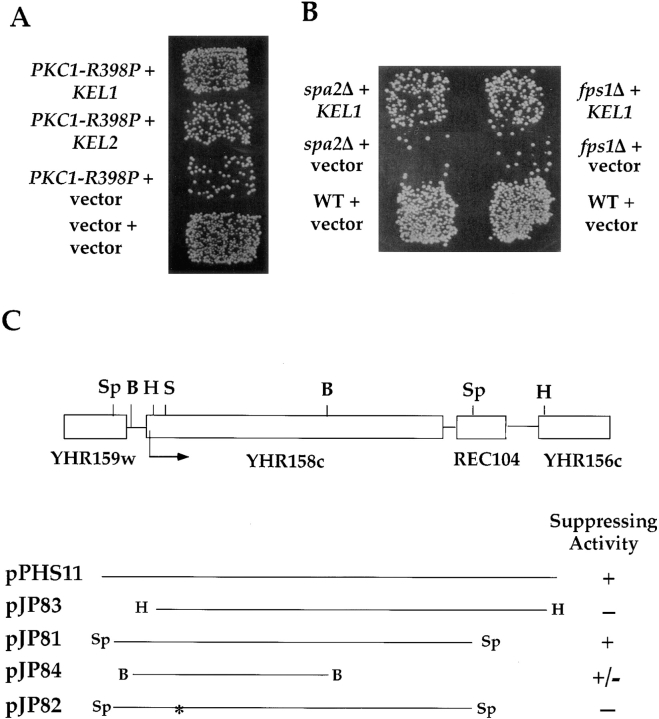
Identification of KEL1 and KEL2 as suppressors of PKC1-R398P. (A) High-copy KEL1 and KEL2 suppress the mating defect associated with PKC1-R398P. JP317 (MATa PKC1-R398P) carrying 2μ plasmids containing KEL1 (pJP81), KEL2 (pJP92), or vector (YEp351) were mated to a MATα fus1 fus2 strain (IH2351) as described in Materials and Methods. The wild-type control (JP338) harbored vector YEp351. (B) High-copy KEL1 suppresses the mating defect of spa2Δ and fps1Δ mutants. spa2Δ (IH3204) and fps1Δ (JP147) mutants harboring 2μ plasmids containing KEL1 (pJP81) or vector (YEp351) were mated to MATα fus1 fus2 strain (IH2351) as described in Materials and Methods. The wild-type strain (IH3196) contained vector (YEp351). (C) Restriction map and subcloning analysis of pPHS11. pPHS11 is the original plasmid obtained from the high-copy suppressor screen. pJP81-84 are YEp351-derived plasmids carrying the indicated segments. pJP82 was generated by digesting pJP81 with SpeI, filling in with Klenow (*), and religating to destroy the reading frame of YHR158c. The ability of each plasmid to suppress the mating defect of JP317 is indicated on the right: +, suppression; −, no suppression; ±, partial suppression. Restriction enzymes: S, SpeI; B, BamHI; H, HindIII; Sp, SphI. Additional information is provided in Materials and Methods and in the text.