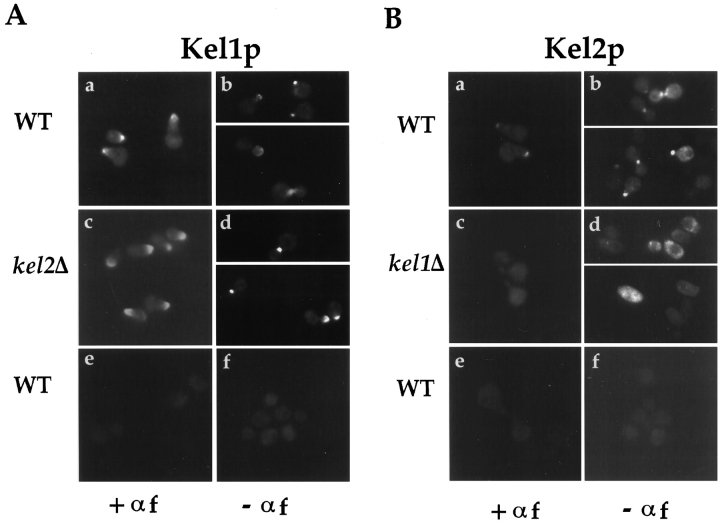
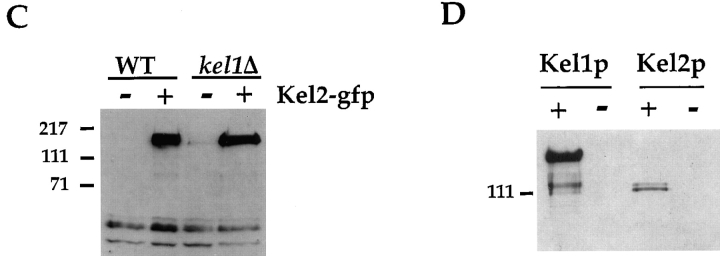
Figure 3.
Localization of Kel1p and Kel2p. (A) An integrating plasmid containing Kel1p-GFP (pJP139) was used to localize Kel1p in wild-type cells (IH3196) (a and b) and in kel2Δ (JP370) cells (c and d). No signal was observed in wild-type cells expressing an untagged control plasmid (pJP143) (e and f). Cells in a, c, and e were treated with 25 μg/ml α-factor for ∼2 h. b, d, and f are composites from two different photographs. (B) YEp351 containing Kel2p-GFP (pJP126) was used to localize Kel2p in wild-type cells (a and b) and in kel1Δ cells (JP363; c and d). No signal was observed in wild-type cells expressing an untagged control plasmid (pJP123; e and f). Cells in a, c, and e were treated with 25 μg/ml α-factor for ∼2 h. b, d, and f are composites from two different photographs. (C) Kel2p is present in kel1Δ strains. Wild-type (IH3196) and kel1Δ (JP363) strains harboring plasmids encoding Kel2p-GFP (pJP126) or untagged control plasmid (pJP123) were analyzed by Western blot as described in Materials and Methods. Monoclonal antibodies recognizing GFP (C163) were a generous gift from P. O'Farrell. Molecular weight standards are indicated on the left. (D) Kel1p is more highly expressed than Kel2p. JP317 was transformed with YEp351-derived plasmids containing Kel1p-HA (pJP202), untagged Kel1p (pJP127), Kel2p-HA (pJP131), or untagged Kel2p (pJP123). +, HA-tagged versions; −, untagged versions. Extracts were prepared as described in Materials and Methods. Lanes were equally loaded, and Western blot analysis was performed with monoclonal antibodies recognizing the HA tag (HA11; Berkeley Antibody Co., Inc.). Molecular weight standards are indicated on the left.