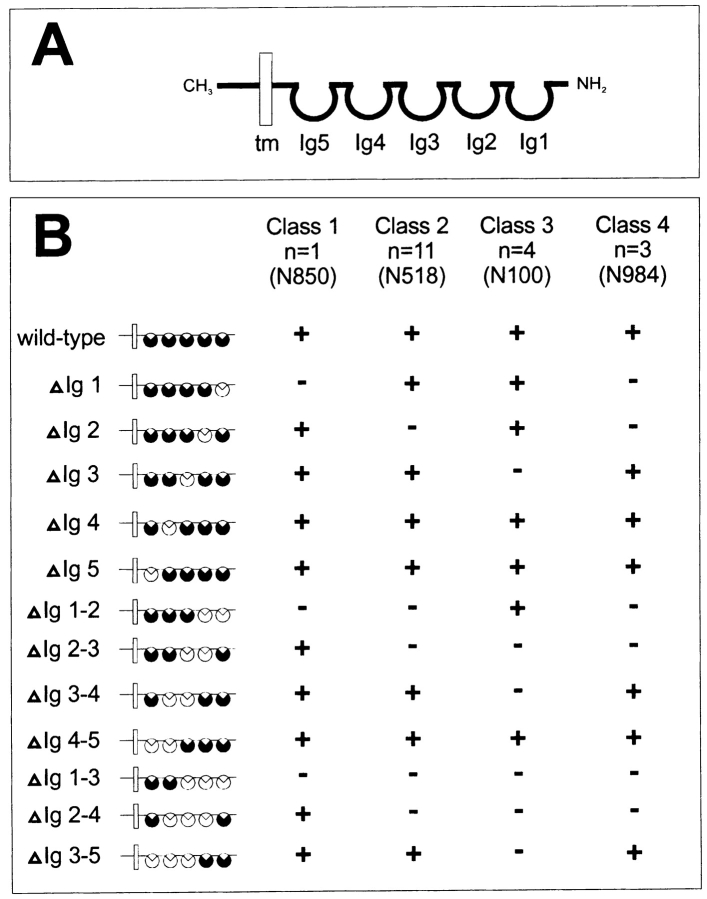
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of neurolin deletion clones and the binding properties of neurolin mAbs. (A) Wild-type neurolin consists of five Ig domains (Ig1–Ig5, black circles), a transmembrane domain (tm), and a short intracellular domain (carboxy terminus, CH3). (B) mAbs against neurolin were screened for their ability (+) or failure (−) to bind to CHO cells expressing forms of neurolin (ΔIg1, ΔIg2, etc.) from which either one, two, or three consecutive Ig domains are deleted (white circles). mAbs fall into four classes: mAbs of class 1 require the presence of Ig domain 1; mAbs of class 2, Ig domain 2; mAbs of class 3, Ig domain 3; and mAbs of class 4, Ig domains 1 and 2 (n, number of mAbs in this class). mAbs N850, N518, N100, and N984 of classes 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively, were used in functional assays.